Evaluation of cell death pathways initiated by antitumor drugs melatonin and valproic acid in bladder cancer cells
- PMID: 28593135
- PMCID: PMC5458469
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.12223
Evaluation of cell death pathways initiated by antitumor drugs melatonin and valproic acid in bladder cancer cells
Abstract
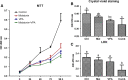
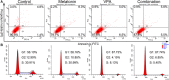
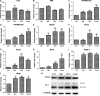
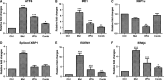
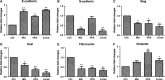
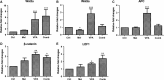
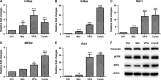
Effective drug combinations have the potential to strengthen therapeutic efficacy and combat drug resistance. Both melatonin and valproic acid (VPA) exhibit antitumor activities in various cancer cells. The aim of this study was to evaluate the cell death pathways initiated by anticancer combinatorial effects of melatonin and VPA in bladder cancer cells. The results demonstrated that the combination of melatonin and VPA leads to significant synergistic growth inhibition of UC3 bladder cancer cells. Gene expression studies revealed that cotreatment with melatonin and VPA triggered the up-regulation of certain genes related to apoptosis (TNFRSF10A and TNFRSF10B), autophagy (BECN, ATG3 and ATG5) and necrosis (MLKL, PARP-1 and RIPK1). The combinatorial treatment increased the expression of endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-stress-related genes ATF6, IRE1, EDEM1 and ERdj4. Cotreatment with melatonin and VPA enhanced the expression of E-cadherin, and decreased the expression of N-cadherin, Fibronectin, Snail and Slug. Furthermore, the Wnt pathway and Raf/MEK/ERK pathway were activated by combinatorial treatment. However, the effects on the expression of certain genes were not further enhanced in cells following combinatorial treatment in comparison to individual treatment of melatonin or VPA. In summary, these findings provided evidence that cotreatment with melatonin and VPA exerted increased cytotoxicity by regulating cell death pathways in UC3 bladder cancer cells, but the clinical significance of combinatorial treatment still needs to be further exploited.
Keywords: ER stress; apoptosis; autophagy; epithelial–mesenchymal transition; melatonin; valproic acid.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Melatonin and urological cancers: a new therapeutic approach.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Sep 10;20:444. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01531-1. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32943992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel targets for valproic acid: up-regulation of melatonin receptors and neurotrophic factors in C6 glioma cells.J Neurochem. 2005 Dec;95(5):1227-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03457.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 16313512
-
Valproic acid, an anti-epileptic drug and a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in combination with proteasome inhibitors exerts antiproliferative, pro-apoptotic and chemosensitizing effects in human colorectal cancer cells: underlying molecular mechanisms.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Aug;34(2):513-32. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1795. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24899129
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid (VPA) promotes the epithelial mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells via up regulation of Snail.Cell Adh Migr. 2015;9(6):495-501. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2015.1112486. Cell Adh Migr. 2015. PMID: 26632346 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin and endoplasmic reticulum stress: relation to autophagy and apoptosis.J Pineal Res. 2015 Oct;59(3):292-307. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12264. Epub 2015 Aug 9. J Pineal Res. 2015. PMID: 26201382 Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin Enhances Palladium-Nanoparticle-Induced Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis in Human Lung Epithelial Adenocarcinoma Cells A549 and H1229.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Apr 24;9(4):357. doi: 10.3390/antiox9040357. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32344592 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis and Cancer: Complex Relationship and Potential Application of Exosomes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 8;9:733751. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.733751. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34568341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin and urological cancers: a new therapeutic approach.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Sep 10;20:444. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01531-1. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32943992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the Differential Effects of Valproic Acid on Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Adv Pharm Bull. 2019 Aug;9(3):497-504. doi: 10.15171/apb.2019.059. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Adv Pharm Bull. 2019. PMID: 31592436 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin Suppresses Ferroptosis Induced by High Glucose via Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in Type 2 Diabetic Osteoporosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Dec 4;2020:9067610. doi: 10.1155/2020/9067610. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33343809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Kessel KE, Zuiverloon TC, Alberts AR, Boormans JL and Zwarthoff EC (2015) Targeted therapies in bladder cancer: an overview of in vivo research. Nat Rev Urol 12, 681–694. - PubMed
-
- Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Manchester LC and Qi W (2001) Biochemical reactivity of melatonin with reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: a review of the evidence. Cell Biochem Biophys 34, 237–256. - PubMed
-
- Zou DB, Wei X, Hu RL, Yang XP, Zou L, Zhang SM, Zhu HQ, Zhou Q, Gui SY and Wang Y (2015) Melatonin inhibits the migration of colon cancer RKO cells by down‐regulating myosin light chain kinase expression through cross‐talk with p38 MAPK. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16, 5835–5842. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

