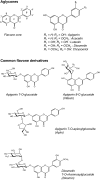
Flavones: Food Sources, Bioavailability, Metabolism, and Bioactivity
- PMID: 28507008
- PMCID: PMC5421117
- DOI: 10.3945/an.116.012948
Flavones: Food Sources, Bioavailability, Metabolism, and Bioactivity
Abstract
Flavones are a class of flavonoids that are a subject of increasing interest because of their biological activities in vitro and in vivo. This article reviews the major sources of flavones and their concentrations in food and beverages, which vary widely between studies. It also covers the roles of flavones in plants, the influence of growing conditions on their concentrations, and their stability during food processing. The absorption and metabolism of flavones are also reviewed, in particular the intestinal absorption of both O- and C-glycosides. Pharmacokinetic studies in both animals and humans are described, comparing differences between species and the effects of glycosylation on bioavailability. Biological activity in animal models and human dietary intervention studies is also reviewed. A better understanding of flavone sources and bioavailability is needed to understand mechanisms of action and nutritional intervention.
Keywords: absorption; apigenin; diosmetin; flavonoids; luteolin; metabolism; pharmacokinetics.
© 2017 American Society for Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
2: Author disclosures: GL Hostetler, RA Ralston, and SJ Schwartz, no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methylation of dietary flavones greatly improves their hepatic metabolic stability and intestinal absorption.Mol Pharm. 2007 Nov-Dec;4(6):826-32. doi: 10.1021/mp700071d. Epub 2007 Oct 25. Mol Pharm. 2007. PMID: 17958394 Review.
-
A combined strategy of mass fragmentation, post-column cobalt complexation and shift in ultraviolet absorption spectra to determine the uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase metabolism profiling of flavones after oral administration of a flavone mixture in rats.J Chromatogr A. 2015 May 22;1395:116-28. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.03.069. Epub 2015 Apr 1. J Chromatogr A. 2015. PMID: 25892633
-
Flavone deglycosylation increases their anti-inflammatory activity and absorption.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012 Apr;56(4):558-69. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201100596. Epub 2012 Feb 20. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012. PMID: 22351119 Free PMC article.
-
[Bioavailability and metabolism of flavonoids].Eksp Klin Farmakol. 2011;74(6):33-40. Eksp Klin Farmakol. 2011. PMID: 21870774 Review. Russian.
-
Plasma Pharmacokinetics, Bioavailability, and Tissue Distribution of Four C-Glycosyl Flavones from Mung Bean (Vigna radiata L.) Seed Extracts in Rat by Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry.J Agric Food Chem. 2017 Jul 12;65(27):5570-5580. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02053. Epub 2017 Jun 28. J Agric Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 28627167
Cited by
-
Harnessing the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Polyphenols in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Oct 14;20(14):5608-5672. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.98107. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39494333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
(E)-1-(2-Hy-droxy-4,6-di-meth-oxy-phen-yl)-3-(naph-thalen-1-yl)prop-2-en-1-one.IUCrdata. 2022 Sep 27;7(Pt 9):x220932. doi: 10.1107/S2414314622009324. eCollection 2022 Sep. IUCrdata. 2022. PMID: 36337459 Free PMC article.
-
Ensemble-based screening of natural products and FDA-approved drugs identified potent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 that work with two distinct mechanisms.J Mol Graph Model. 2021 Jun;105:107871. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2021.107871. Epub 2021 Feb 23. J Mol Graph Model. 2021. PMID: 33684603 Free PMC article.
-
Taxillus chinensis (DC.) Danser: a comprehensive review on botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology.Chin Med. 2022 Dec 8;17(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00694-5. Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 36482376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mediterranean Diet and Neurodegenerative Diseases: The Neglected Role of Nutrition in the Modulation of the Endocannabinoid System.Biomolecules. 2021 May 24;11(6):790. doi: 10.3390/biom11060790. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34073983 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hollman PCH. Absorption, bioavailability, and metabolism of flavonoids. Pharm Biol 2004;42:74–83.
-
- Manach C, Scalbert A, Morand C, Remesy C, Jimenez L. Polyphenols: food sources and bioavailability. Am J Clin Nutr 2004;79:727–47. - PubMed
-
- Manach C, Williamson G, Morand C, Scalbert A, Remesy C. Bioavailability and bioefficacy of polyphenols in humans. I. Review of 97 bioavailability studies. Am J Clin Nutr 2005;81:230S–242S. - PubMed
-
- Williamson G, Manach C. Bioavailability and bioefficacy of polyphenols in humans. II. Review of 93 intervention studies. Am J Clin Nutr 2005;81:243S–255S. - PubMed
-
- Martens S, Mithöfer A. Flavones and flavone synthases. Phytochemistry 2005;66:2399–407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources