IFI16 and cGAS cooperate in the activation of STING during DNA sensing in human keratinocytes
- PMID: 28194029
- PMCID: PMC5316833
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14392
IFI16 and cGAS cooperate in the activation of STING during DNA sensing in human keratinocytes
Abstract
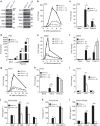
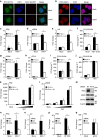
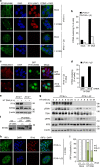
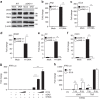
Many human cells can sense the presence of exogenous DNA during infection though the cytosolic DNA receptor cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS), which produces the second messenger cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP). Other putative DNA receptors have been described, but whether their functions are redundant, tissue-specific or integrated in the cGAS-cGAMP pathway is unclear. Here we show that interferon-γ inducible protein 16 (IFI16) cooperates with cGAS during DNA sensing in human keratinocytes, as both cGAS and IFI16 are required for the full activation of an innate immune response to exogenous DNA and DNA viruses. IFI16 is also required for the cGAMP-induced activation of STING, and interacts with STING to promote STING phosphorylation and translocation. We propose that the two DNA sensors IFI16 and cGAS cooperate to prevent the spurious activation of the type I interferon response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IFI16 is required for DNA sensing in human macrophages by promoting production and function of cGAMP.Nat Commun. 2017 Feb 10;8:14391. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14391. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28186168 Free PMC article.
-
Viral DNA Sensors IFI16 and Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase Possess Distinct Functions in Regulating Viral Gene Expression, Immune Defenses, and Apoptotic Responses during Herpesvirus Infection.mBio. 2016 Nov 15;7(6):e01553-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01553-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27935834 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleosomal dsDNA Stimulates APOL1 Expression in Human Cultured Podocytes by Activating the cGAS/IFI16-STING Signaling Pathway.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 29;9(1):15485. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51998-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31664093 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved strategies for pathogen evasion of cGAS-STING immunity.Curr Opin Immunol. 2020 Oct;66:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2020.04.002. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Curr Opin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32339908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate-Adenosine Monophosphate Synthase (cGAS), a Multifaceted Platform of Intracellular DNA Sensing.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 23;12:637399. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.637399. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33708225 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic profile of the mice aging lung is associated with inflammation and apoptosis as important pathways.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 May 12;13(9):12378-12394. doi: 10.18632/aging.203039. Epub 2021 May 12. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33982668 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Sensing Mechanisms that Discriminate Self from Altered Self and Foreign Nucleic Acids.Immunity. 2020 Jul 14;53(1):54-77. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.014. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 32668228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
System-Based Approaches to Delineate the Antiviral Innate Immune Landscape.Viruses. 2020 Oct 21;12(10):1196. doi: 10.3390/v12101196. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33096788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA-PK Is Targeted by Multiple Vaccinia Virus Proteins to Inhibit DNA Sensing.Cell Rep. 2018 Nov 13;25(7):1953-1965.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.034. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30428360 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational Control of Innate Immune Signaling Pathways by Herpesviruses.Front Microbiol. 2019 Nov 14;10:2647. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02647. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31798565 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

