Suppressors of cytokine signaling: Potential immune checkpoint molecules for cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 28188673
- PMCID: PMC5406529
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13194
Suppressors of cytokine signaling: Potential immune checkpoint molecules for cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
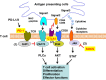
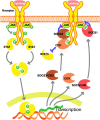
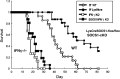
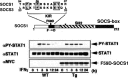
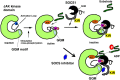
Inhibition of immune checkpoint molecules, PD-1 and CTLA4, has been shown to be a promising cancer treatment. PD-1 and CTLA4 inhibit TCR and co-stimulatory signals. The third T cell activation signal represents the signals from the cytokine receptors. The cytokine interferon-γ (IFNγ) plays an important role in anti-tumor immunity by activating cytotoxic T cells (CTLs). Most cytokines use the Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway, and the suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) family of proteins are major negative regulators of the JAK/STAT pathway. Among SOCS proteins, CIS, SOCS1, and SOCS3 proteins can be considered the third immunocheckpoint molecules since they regulate cytokine signals that control the polarization of CD4+ T cells and the maturation of CD8+ T cells. This review summarizes recent progress on CIS, SOCS1, and SOCS3 in terms of their anti-tumor immunity and potential applications.
Keywords: Immune checkpoint; JAK-STAT; T cell; kinase inhibitory region; suppressors of cytokine signaling.
© 2017 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins and JAK/STAT pathways: regulation of T-cell inflammation by SOCS1 and SOCS3.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 May;31(5):980-5. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.207464. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21508344 Review.
-
Japanese encephalitis virus infection modulates the expression of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) in macrophages: implications for the hosts' innate immune response.Cell Immunol. 2013 Sep-Oct;285(1-2):100-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2013.09.005. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Cell Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24140964
-
Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling Proteins 3 and 5 Potentially Delineate Polarization of Th cells in Chronic Rhinosinusitis.Yale J Biol Med. 2024 Jun 28;97(2):165-177. doi: 10.59249/HZFN2950. eCollection 2024 Jun. Yale J Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 38947108 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressors of cytokine signaling modulate JAK/STAT-mediated cell responses during atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009 Apr;29(4):525-31. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.173781. Epub 2009 Jan 22. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19164812
-
SOCS1 and SOCS3 as key checkpoint molecules in the immune responses associated to skin inflammation and malignant transformation.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 21;15:1393799. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1393799. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38975347 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer Stem Cells: From an Insight into the Basics to Recent Advances and Therapeutic Targeting.Stem Cells Int. 2022 Jun 28;2022:9653244. doi: 10.1155/2022/9653244. eCollection 2022. Stem Cells Int. 2022. PMID: 35800881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JAK/STAT signaling in diabetic kidney disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Aug 11;11:1233259. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1233259. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37635867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telmisartan mitigates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced production of mucin 5AC (MUC5AC) through increasing suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1).Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):3912-3923. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1943605. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34281463 Free PMC article.
-
Individual and Synergistic Anti-Coronavirus Activities of SOCS1/3 Antagonist and Interferon α1 Peptides.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 21;13:902956. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.902956. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35799776 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting cancer stem cell pathways for cancer therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Feb 7;5(1):8. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0110-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32296030 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ikeda H, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. The roles of IFN gamma in protection against tumor development and cancer immunoediting. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2002; 13: 95–109. - PubMed
-
- O'Shea JJ, Gadina M, Schreiber RD. Cytokine signaling in 2002: new surprises in the Jak/Stat pathway. Cell 2002; 109(Suppl): S121–31. - PubMed
-
- Weber‐Nordt RM, Riley JK, Greenlund AC, Moore KW, Darnell JE, Schreiber RD. Stat3 recruitment by two distinct ligand‐induced, tyrosine‐phosphorylated docking sites in the interleukin‐10 receptor intracellular domain. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 27954–61. - PubMed
-
- Tamiya T, Ichiyama K, Kotani H et al Smad2/3 and IRF4 play a cooperative role in IL‐9‐producing T cell induction. J Immunol 2013; 191: 2360–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

