Hepatitis C Virus Infection of Cultured Human Hepatoma Cells Causes Apoptosis and Pyroptosis in Both Infected and Bystander Cells
- PMID: 27974850
- PMCID: PMC5156923
- DOI: 10.1038/srep37433
Hepatitis C Virus Infection of Cultured Human Hepatoma Cells Causes Apoptosis and Pyroptosis in Both Infected and Bystander Cells
Abstract
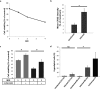
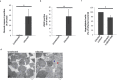
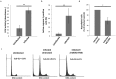
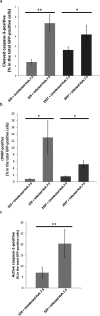
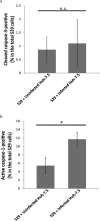
Individuals infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) are at high risk of developing progressive liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). How HCV infection causes liver destruction has been of significant interest for many years, and apoptosis has been proposed as one operative mechanism. In this study, we employed a tissue culture-adapted strain of HCV (JFH1T) to test effects of HCV infection on induction of programmed cell death (PCD) in Huh-7.5 cells. We found that HCV infection reduced the proliferation rate and induced caspase-3-mediated apoptosis in the infected cell population. However, in addition to apoptosis, we also observed infected cells undergoing caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis, which was induced by NLRP3 inflammasome activation. By co-culturing HCV-infected Huh-7.5 cells with an HCV-non-permissive cell line, we also demonstrated induction of both apoptosis and pyroptosis in uninfected cells. Bystander apoptosis, but not bystander pyroptosis, required cell-cell contact between infected and bystander cells. In summary, these findings provide new information on mechanisms of cell death in response to HCV infection. The observation that both apoptosis and pyroptosis can be induced in bystander cells extends our understanding of HCV-induced pathogenesis in the liver.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crosstalk Between Pyroptosis and Apoptosis in Hepatitis C Virus-induced Cell Death.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 14;13:788138. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.788138. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35237259 Free PMC article.
-
The Hepatitis C Virus-induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activates the Sterol Regulatory Element-binding Protein (SREBP) and Regulates Lipid Metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 12;291(7):3254-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.694059. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Biol Chem. 2016. Retraction in: J Biol Chem. 2018 Dec 28;293(52):20011. doi: 10.1074/jbc.W118.006979 PMID: 26698881 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Enterococcus faecalis induces apoptosis and pyroptosis of human osteoblastic MG63 cells via the NLRP3 inflammasome.Int Endod J. 2019 Jan;52(1):44-53. doi: 10.1111/iej.12965. Epub 2018 Jun 29. Int Endod J. 2019. PMID: 29904931
-
Inflammasomes and its importance in viral infections.Immunol Res. 2016 Dec;64(5-6):1101-1117. doi: 10.1007/s12026-016-8873-z. Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27699580 Review.
-
Inflammatory Consequences: Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Inflammasome Activation and Pyroptosis.Viral Immunol. 2024 Apr;37(3):126-138. doi: 10.1089/vim.2023.0138. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Viral Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38593460 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Mechanisms Associated with Chronic HCV Infection and the Impact of Direct-Acting Antiviral Treatment.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2020 Apr 15;7:45-76. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S221187. eCollection 2020. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2020. PMID: 32346535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating network pharmacology and experimental validation to decipher the mechanism of the Chinese herbal prescription JieZe-1 in protecting against HSV-2 infection.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):451-466. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2038209. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35180012 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Death in Coronavirus Infections: Uncovering Its Role during COVID-19.Cells. 2021 Jun 23;10(7):1585. doi: 10.3390/cells10071585. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34201847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of elevated serum and hepatic NOD-like receptor pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) in hepatitis C virus-related liver disease.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 14;12(1):19528. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22022-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36376416 Free PMC article.
-
HCV-induced autophagy and innate immunity.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 2;15:1305157. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1305157. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38370419 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marcellin P. Hepatitis C: the clinical spectrum of the disease. Journal of hepatology 31 Suppl 1, 9–16 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

