Dioxin induces Ahr-dependent robust DNA demethylation of the Cyp1a1 promoter via Tdg in the mouse liver
- PMID: 27713569
- PMCID: PMC5054525
- DOI: 10.1038/srep34989
Dioxin induces Ahr-dependent robust DNA demethylation of the Cyp1a1 promoter via Tdg in the mouse liver
Abstract
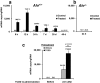
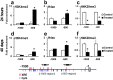
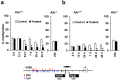
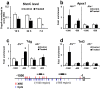
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr) is a highly conserved nuclear receptor that plays an important role in the manifestation of toxicity induced by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. As a xenobiotic sensor, Ahr is involved in chemical biotransformation through activation of drug metabolizing enzymes. The activated Ahr cooperates with coactivator complexes to induce epigenetic modifications at target genes. Thus, it is conceivable that 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), a potent Ahr ligand, may elicit robust epigenetic changes in vivo at the Ahr target gene cytochrome P450 1a1 (Cyp1a1). A single dose of TCDD administered to adult mice induced Ahr-dependent CpG hypomethylation, changes in histone modifications, and thymine DNA glycosylase (Tdg) recruitment at the Cyp1a1 promoter in the liver within 24 hrs. These epigenetic changes persisted until 40 days post-TCDD treatment and there was Cyp1a1 mRNA hyperinduction upon repeat administration of TCDD at this time-point. Our demethylation assay using siRNA knockdown and an in vitro methylated plasmid showed that Ahr, Tdg, and the ten-eleven translocation methyldioxygenases Tet2 and Tet3 are required for the TCDD-induced DNA demethylation. These results provide novel evidence of Ahr-driven active DNA demethylation and epigenetic memory. The epigenetic alterations influence response to subsequent chemical exposure and imply an adaptive mechanism to xenobiotic stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoxia perturbs aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling and CYP1A1 expression induced by PCB 126 in human skin and liver-derived cell lines.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Feb 1;274(3):408-16. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24355420 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression and activity in cerebellar granule neuroblasts: implications for development and dioxin neurotoxicity.Toxicol Sci. 2005 Feb;83(2):340-8. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfi031. Epub 2004 Nov 10. Toxicol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15537747
-
TCDD-induced expression of Ah receptor responsive genes in the pituitary and brain of cellular retinol-binding protein (CRBP-I) knockout mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2003 Nov 1;192(3):262-74. doi: 10.1016/s0041-008x(03)00296-5. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14575644
-
Functional role of AhR in the expression of toxic effects by TCDD.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003 Feb 17;1619(3):263-8. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(02)00485-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003. PMID: 12573486 Review.
-
Role of coactivators in transcriptional activation by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005 Jan 15;433(2):379-86. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2004.09.031. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005. PMID: 15581594 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential methylation pattern of xenobiotic metabolizing genes and susceptibility to Balkan endemic nephropathy, in a cohort of Romanian patients.J Nephrol. 2020 Feb;33(1):91-100. doi: 10.1007/s40620-019-00621-2. Epub 2019 Jun 20. J Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31222646
-
The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor, Epigenetics and the Aging Process.J Nutr Health Aging. 2023;27(4):291-300. doi: 10.1007/s12603-023-1908-1. J Nutr Health Aging. 2023. PMID: 37170437 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour Microenvironment: Roles of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor, O-GlcNAcylation, Acetyl-CoA and Melatonergic Pathway in Regulating Dynamic Metabolic Interactions across Cell Types-Tumour Microenvironment and Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 25;22(1):141. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010141. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33375613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sp1, Instead of AhR, Regulates the Basal Transcription of Porcine CYP1A1 at the Proximal Promoter.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Aug 17;9:927. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00927. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30174605 Free PMC article.
-
TCDD Toxicity Mediated by Epigenetic Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 18;19(12):4101. doi: 10.3390/ijms19124101. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30567322 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mimura J. & Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Functional role of AhR in the expression of toxic effects by TCDD. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Gen. Subj. 1619, 263–268 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Gu Y. Z., Hogenesch J. B. & Bradfield C. A. The PAS superfamily: sensors of environmental and developmental signals. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 40, 519–561 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Stockinger B., Di Meglio P., Gialitakis M. & Duarte J. H. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: multitasking in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 32, 403–432 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

