MicroRNA-223 ameliorates alcoholic liver injury by inhibiting the IL-6-p47phox-oxidative stress pathway in neutrophils
- PMID: 27679493
- PMCID: PMC5458746
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-311861
MicroRNA-223 ameliorates alcoholic liver injury by inhibiting the IL-6-p47phox-oxidative stress pathway in neutrophils
Abstract
Objectives: Chronic-plus-binge ethanol feeding activates neutrophils and exacerbates liver injury in mice. This study investigates how recent excessive drinking affects peripheral neutrophils and liver injury in alcoholics, and how miR-223, one of the most abundant microRNAs (miRNAs) in neutrophils, modulates neutrophil function and liver injury in ethanol-fed mice.
Designs: Three hundred alcoholics with (n=140) or without (n=160) recent excessive drinking and 45 healthy controls were enrolled. Mice were fed an ethanol diet for 10 days followed by a single binge of ethanol.
Results: Compared with healthy controls or alcoholics without recent drinking, alcoholics with recent excessive drinking had higher levels of circulating neutrophils, which correlated with serum levels of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST). miRNA array analysis revealed that alcoholics had elevated serum miR-223 levels compared with healthy controls. In chronic-plus-binge ethanol feeding mouse model, the levels of miR-223 were increased in both serum and neutrophils. Genetic deletion of the miR-223 gene exacerbated ethanol-induced hepatic injury, neutrophil infiltration, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and upregulated hepatic expression of interleukin (IL)-6 and phagocytic oxidase (phox) p47phox. Mechanistic studies revealed that miR-223 directly inhibited IL-6 expression and subsequently inhibited p47phox expression in neutrophils. Deletion of the p47phox gene ameliorated ethanol-induced liver injury and ROS production by neutrophils. Finally, miR-223 expression was downregulated, while IL-6 and p47phox expression were upregulated in peripheral blood neutrophils from alcoholics compared with healthy controls.
Conclusions: miR-223 is an important regulator to block neutrophil infiltration in alcoholic liver disease and could be a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of this malady.
Keywords: CYTOKINES; ETHANOL; FATTY LIVER; INFLAMMATION; LEUKOCYTES.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
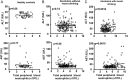
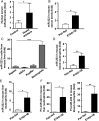
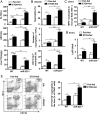
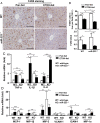
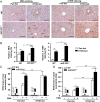
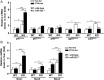
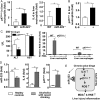
Comment in
-
A small RNA in neutrophils protects against acute-on-chronic alcoholic liver injury.Gut. 2017 Apr;66(4):565-566. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312966. Epub 2016 Oct 8. Gut. 2017. PMID: 27802158 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-22 treatment ameliorates alcoholic liver injury in a murine model of chronic-binge ethanol feeding: role of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.Hepatology. 2010 Oct;52(4):1291-300. doi: 10.1002/hep.23837. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20842630 Free PMC article.
-
Aging exaggerates acute-on-chronic alcohol-induced liver injury in mice and humans by inhibiting neutrophilic sirtuin 1-C/EBPα-miRNA-223 axis.Hepatology. 2022 Mar;75(3):646-660. doi: 10.1002/hep.32152. Epub 2021 Dec 5. Hepatology. 2022. PMID: 34510484 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise Affects the Formation and Recovery of Alcoholic Liver Disease through the IL-6-p47phox Oxidative-Stress Axis.Cells. 2022 Apr 12;11(8):1305. doi: 10.3390/cells11081305. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35455983 Free PMC article.
-
Animals models of gastrointestinal and liver diseases. Animal models of alcohol-induced liver disease: pathophysiology, translational relevance, and challenges.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 May 15;306(10):G819-23. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00041.2014. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24699333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity and binge alcohol intake are deadly combination to induce steatohepatitis: A model of high-fat diet and binge ethanol intake.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020 Oct;26(4):586-594. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2020.0100. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32937687 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-223-3p inhibits vascular calcification and the osteogenic switch of vascular smooth muscle cells.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100483. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100483. Epub 2021 Feb 26. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33647318 Free PMC article.
-
Kupffer Cells: Inflammation Pathways and Cell-Cell Interactions in Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease.Am J Pathol. 2020 Nov;190(11):2185-2193. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.08.014. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Am J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32919978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome prospects in the diagnosis and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 31;11:1420281. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1420281. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39144666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Changes in Relation to Alcohol Consumption and Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 26;23(17):9679. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179679. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A small RNA in neutrophils protects against acute-on-chronic alcoholic liver injury.Gut. 2017 Apr;66(4):565-566. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312966. Epub 2016 Oct 8. Gut. 2017. PMID: 27802158 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
