Microtubule destabilising agents: far more than just antimitotic anticancer drugs
- PMID: 27620987
- PMCID: PMC5237681
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13126
Microtubule destabilising agents: far more than just antimitotic anticancer drugs
Abstract
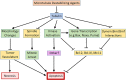
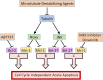
Vinca alkaloids have been approved as anticancer drugs for more than 50 years. They have been classified as cytotoxic chemotherapy drugs that act during cellular mitosis, enabling them to target fast growing cancer cells. With the evolution of cancer drug development there has been a shift towards new "targeted" therapies to avoid the side effects and general toxicities of "cytotoxic chemotherapies" such as the vinca alkaloids. Due to their original classification, many have overlooked the fact that vinca alkaloids, taxanes and related drugs do have a specific molecular target: tubulin. They continue to be some of the most effective anticancer drugs, perhaps because their actions upon the microtubule network extend far beyond the ability to halt cells in mitosis, and include the induction of apoptosis at all phases of the cell cycle. In this review, we highlight the numerous cellular consequences of disrupting microtubule dynamics, expanding the textbook knowledge of microtubule destabilising agents and providing novel opportunities for their use in cancer therapy.
Keywords: Bcl-2; apoptosis; c-Jun N-terminal kinase; colchicine; microtubule destabilising agents; vinca alkaloids.
© 2016 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microtubule inhibitors: Differentiating tubulin-inhibiting agents based on mechanisms of action, clinical activity, and resistance.Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 Aug;8(8):2086-95. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0366. Epub 2009 Aug 11. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009. PMID: 19671735 Review.
-
Natural products as antimitotic agents.Curr Top Med Chem. 2014;14(20):2272-85. doi: 10.2174/1568026614666141130095311. Curr Top Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25434355 Review.
-
Sensitivity of docetaxel-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells to microtubule-destabilizing agents including vinca alkaloids and colchicine-site binding agents.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 7;12(8):e0182400. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182400. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28787019 Free PMC article.
-
6α-Acetoxyanopterine: A Novel Structure Class of Mitotic Inhibitor Disrupting Microtubule Dynamics in Prostate Cancer Cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Jan;16(1):3-15. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0325. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 27760837
-
Tubulin and microtubules as targets for anticancer drugs.Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2003;5:309-25. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2003. PMID: 14593726 Review.
Cited by
-
Herbal Therapies for Cancer Treatment: A Review of Phytotherapeutic Efficacy.Biologics. 2024 Sep 10;18:229-255. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S484068. eCollection 2024. Biologics. 2024. PMID: 39281032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of the novel tubulin polymerization inhibitor PTC-028 for myelodysplastic syndrome.Cancer Sci. 2020 Dec;111(12):4336-4347. doi: 10.1111/cas.14684. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 33037737 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of microtubules in invasion plasticity.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 13;13:1118171. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1118171. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36860323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex Formation with Monomeric α-Tubulin and Importin 13 Fosters c-Jun Protein Stability and Is Required for c-Jun's Nuclear Translocation and Activity.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 17;11(11):1806. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111806. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31744174 Free PMC article.
-
5-arylalkynyl-2-benzoyl thiophene: a novel microtubule inhibitor exhibits antitumor activity without neurological toxicity.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Jan 15;12(1):229-246. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35141015 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

