Cytoskeleton-Dependent Transport as a Potential Target for Interfering with Post-transcriptional HuR mRNA Regulons
- PMID: 27582706
- PMCID: PMC4987335
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00251
Cytoskeleton-Dependent Transport as a Potential Target for Interfering with Post-transcriptional HuR mRNA Regulons
Abstract
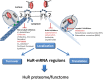
The ubiquitous mRNA binding protein human antigen R (HuR), a member of the embryonal lethal abnormal vision protein family has a critical impact on the post-transcriptional control of AU-rich element bearing mRNA regulons implied in inflammation, senescence, and carcinogenesis. HuR in addition to mRNA stability can affect many other aspects of mRNA processing including splicing, polyadenylation, translation, modulation of miRNA repression, and intracellular mRNA trafficking. Since many of the identified HuR mRNA targets ("HuR mRNA regulons") encode tumor-related proteins, HuR is not only discussed as an useful biomarker but also as promising therapeutic target for treatment of various human cancers. HuR which is most abundantly localized in the nucleus is translocated to the cytoplasm which is fundamental for most of the described HuR functions on target mRNAs. Accordingly, an elevation in cytoplasmic HuR was found in many tumors and correlated with a high grade of malignancy and a poor prognosis of patients. Therefore, direct interference with the intracellular trafficking of HuR offers an attractive approach to intervene with pathologically deregulated HuR functions. Data from several laboratories implicate that the integrity of the cytoskeleton is critical for HuR-mediated intracellular mRNA localization and translation. This review will particularly focus on drugs which have proven a direct inhibitory effect on HuR translocation. Based on the results from those studies, we will also discuss on the principle value of targeting cytoskeleton-dependent transport of HuR by natural or synthetic inhibitors as a potential therapeutic avenue for interfering with dysregulated post-transcriptional HuR mRNA regulons and related tumor cell functions. In spite of that, interfering with cytoplasmic HuR transport could highlight a so far underestimated action of microtubule inhibitors clinically used for cancer chemotherapy.
Keywords: HuR; RNA binding protein; cytoskeleton inhibitors; mRNA stability; mRNA trafficking.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of the mRNA-binding protein HuR by posttranslational modification: spotlight on phosphorylation.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012 Jun;13(4):380-90. doi: 10.2174/138920312801619439. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 22708484 Review.
-
The cytoskeletal inhibitors latrunculin A and blebbistatin exert antitumorigenic properties in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by interfering with intracellular HuR trafficking.Exp Cell Res. 2015 Jan 1;330(1):66-80. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Sep 21. Exp Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 25240929
-
HuR translocation to the cytoplasm of cancer cells in actin-independent manner.Exp Cell Res. 2018 Aug 15;369(2):218-225. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.05.021. Epub 2018 May 26. Exp Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 29807023
-
Signalling pathways regulating nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of the mRNA-binding protein HuR.Cell Signal. 2008 Dec;20(12):2165-73. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.05.007. Epub 2008 May 23. Cell Signal. 2008. PMID: 18585896 Review.
-
The RNA Binding Protein HuR: A Promising Drug Target for Anticancer Therapy.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2019;19(5):382-399. doi: 10.2174/1568009618666181031145953. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 30381077 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of mRNA stability by RBPs and noncoding RNAs contributing to the pathogenicity of Th17 cells.RNA Biol. 2021 May;18(5):647-656. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1862567. Epub 2020 Dec 23. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33302787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of cytokine and growth factor signaling in cancer.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017 Feb;33:83-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.11.004. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017. PMID: 27956133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advantages of Using Paclitaxel in Combination with Oncolytic Adenovirus Utilizing RNA Destabilization Mechanism.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 12;12(5):1210. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051210. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32408515 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding protein HuR enhances mineralocorticoid signaling in renal KC3AC1 cells under hypotonicity.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Dec;74(24):4587-4597. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2594-x. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28744670 Free PMC article.
-
WASH regulates the oxidative stress Nrf2/ARE pathway to inhibit proliferation and promote apoptosis of HeLa cells under the action of Jolkinolide B.PeerJ. 2022 Jul 13;10:e13499. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13499. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35855902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antic D., Keene J. D. (1998). Messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes containing human ELAV proteins: interactions with cytoskeleton and translational apparatus. J. Cell Sci. 111 183–197. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

