Revisiting the Lamotrigine-Mediated Effect on Hippocampal GABAergic Transmission
- PMID: 27455251
- PMCID: PMC4964560
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17071191
Revisiting the Lamotrigine-Mediated Effect on Hippocampal GABAergic Transmission
Abstract
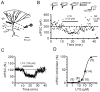
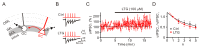
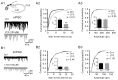
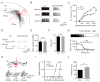
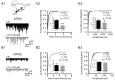
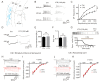
Lamotrigine (LTG) is generally considered as a voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channel blocker. However, recent studies suggest that LTG can also serve as a hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel enhancer and can increase the excitability of GABAergic interneurons (INs). Perisomatic inhibitory INs, predominantly fast-spiking basket cells (BCs), powerfully inhibit granule cells (GCs) in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Notably, BCs express abundant Nav channels and HCN channels, both of which are able to support sustained action potential generation. Using whole-cell recording in rat hippocampal slices, we investigated the net LTG effect on BC output. We showed that bath application of LTG significantly decreased the amplitude of evoked compound inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) in GCs. In contrast, simultaneous paired recordings from BCs to GCs showed that LTG had no effect on both the amplitude and the paired-pulse ratio of the unitary IPSCs, suggesting that LTG did not affect GABA release, though it suppressed cell excitability. In line with this, LTG decreased spontaneous IPSC (sIPSC) frequency, but not miniature IPSC frequency. When re-examining the LTG effect on GABAergic transmission in the cornus ammonis region 1 (CA1) area, we found that LTG markedly inhibits both the excitability of dendrite-targeting INs in the stratum oriens and the concurrent sIPSCs recorded on their targeting pyramidal cells (PCs) without significant hyperpolarization-activated current (Ih) enhancement. In summary, LTG has no effect on augmenting Ih in GABAergic INs and does not promote GABAergic inhibitory output. The antiepileptic effect of LTG is likely through Nav channel inhibition and the suppression of global neuronal network activity.
Keywords: GABAergic interneuron; Lamotrigine; hyperpolarization-activated current; inhibitory postsynaptic current; voltage-gated sodium channel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased basal synaptic inhibition of hippocampal area CA1 pyramidal neurons by an antiepileptic drug that enhances I(H).Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010 Jan;35(2):464-72. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.150. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010. PMID: 19776733 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA receptor activation enhances inhibitory GABAergic transmission onto hippocampal pyramidal neurons via presynaptic and postsynaptic mechanisms.J Neurophysiol. 2011 Jun;105(6):2897-906. doi: 10.1152/jn.00287.2010. Epub 2011 Apr 6. J Neurophysiol. 2011. PMID: 21471392
-
PKC activators enhance GABAergic neurotransmission and paired-pulse facilitation in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons.Neuroscience. 2014 May 30;268:75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.03.008. Epub 2014 Mar 15. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24637095
-
Neurochemical and behavioral aspects of lamotrigine.Epilepsia. 1991;32 Suppl 2:S4-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1991.tb05882.x. Epilepsia. 1991. PMID: 1685439 Review.
-
Cellular and molecular actions of lamotrigine: Possible mechanisms of efficacy in bipolar disorder.Neuropsychobiology. 1998 Oct;38(3):119-30. doi: 10.1159/000026527. Neuropsychobiology. 1998. PMID: 9778599 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding Lamotrigine's Role in the CNS and Possible Future Evolution.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 23;24(7):6050. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076050. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seizures, behavioral deficits, and adverse drug responses in two new genetic mouse models of HCN1 epileptic encephalopathy.Elife. 2022 Aug 16;11:e70826. doi: 10.7554/eLife.70826. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35972069 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience to anhedonia-passive coping induced by early life experience is linked to a long-lasting reduction of Ih current in VTA dopaminergic neurons.Neurobiol Stress. 2021 Apr 15;14:100324. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2021.100324. eCollection 2021 May. Neurobiol Stress. 2021. PMID: 33937445 Free PMC article.
-
Lamotrigine Attenuates Neuronal Excitability, Depresses GABA Synaptic Inhibition, and Modulates Theta Rhythms in Rat Hippocampus.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 19;22(24):13604. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413604. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948401 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Antiarrhythmic Drugs on Antiepileptic Drug Action-A Critical Review of Experimental Findings.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 7;23(5):2891. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052891. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35270033 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

