Downregulation of the neonatal Fc receptor expression in non-small cell lung cancer tissue is associated with a poor prognosis
- PMID: 27384673
- PMCID: PMC5342352
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10074
Downregulation of the neonatal Fc receptor expression in non-small cell lung cancer tissue is associated with a poor prognosis
Abstract
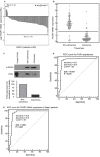
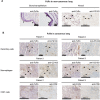
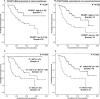
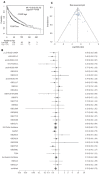
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Although the recommended tumor, node and metastasis (TNM) classification and stage determination are important to select therapeutic options for patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC), additional molecular markers are required to indicate the prognosis, in particular within a specific stage, and help with the management of patients.Because neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) has recently been involved in colon cancer immunosurveillance, we measured its expression in non-cancerous and NSCLC lung tissues and evaluated its prognostic value in overall survival for patient with NSCLC. FcRn expression was determined at both mRNA and protein levels on cancerous and adjacent non-cancerous tissues from 80 NSCLC patients. In NSCLC, FcRn was mainly found in resident and tumor infiltrating immune cells. The corresponding mRNA and protein were significantly less abundant in lung tumor than non-cancerous tissue. Moreover, analysis of our cohort and datasets from the public data bases show that FCGRT mRNA down-regulation is a robust and independent, unfavorable predictive factor of NSCLC patient survival. We conclude that FCGRT mRNA expression may be a useful additional marker for immunoscoring, reflecting tumor immune system, and help in the decision-making process for NSCLC patients.
Keywords: FcRn; antitumor immunity; marker; non-small cell lung cancer; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Down-regulated MicroRNA 148b expression as predictive biomarker and its prognostic significance associated with clinicopathological features in non-small-cell lung cancer patients.Diagn Pathol. 2015 Sep 17;10:164. doi: 10.1186/s13000-015-0393-y. Diagn Pathol. 2015. Retraction in: Diagn Pathol. 2016 Nov 2;11(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13000-016-0562-7. PMID: 26377406 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The neonatal Fc receptor in cancer FcRn in cancer.Cancer Med. 2020 Jul;9(13):4736-4742. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3067. Epub 2020 May 5. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32368865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA HMlincRNA717 is down-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer and associated with poor prognosis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Dec 1;7(12):8881-6. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25674259 Free PMC article.
-
Fc Receptor Expression as a Prognostic Factor in Patients With Non-small-cell Lung Cancer.In Vivo. 2022 Nov-Dec;36(6):2708-2713. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13006. In Vivo. 2022. PMID: 36309388 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of ERCC1 mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and gastric cancer in patients from Southern China.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Dec 1;7(12):8312-21. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25674197 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Receptors and Host Factors for Enterovirus Infection: Implications for Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 12;16(18):3139. doi: 10.3390/cancers16183139. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B cell responses and antibody-based therapeutic perspectives in human cancers.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 Mar;7(3):e2056. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.2056. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38522010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Albumin influences leucocyte FcRn expression in the early days of kidney transplantation.Clin Exp Immunol. 2024 May 16;216(3):307-317. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxae011. Clin Exp Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38353127 Free PMC article.
-
FcRn Expression in Endometrial Cancer and Its Association with Clinicopathologic Features.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Dec 14;13(24):3660. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13243660. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132243 Free PMC article.
-
Single protein encapsulated SN38 for tumor-targeting treatment.J Transl Med. 2023 Dec 10;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04778-0. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 38072965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alifano M, Mansuet-Lupo A, Lococo F, Roche N, Bobbio A, Canny E, Schussler O, Dermine H, Régnard J-F, Burroni B, Goc J, Biton J, Ouakrim H, et al. Systemic inflammation, nutritional status and tumor immune microenvironment determine outcome of resected non-small cell lung cancer. PloS One. 2014;9:e106914. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106914. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Germain C, Gnjatic S, Tamzalit F, Knockaert S, Remark R, Goc J, Lepelley A, Becht E, Katsahian S, Bizouard G, Validire P, Damotte D, Alifano M, et al. Presence of B cells in tertiary lymphoid structures is associated with a protective immunity in patients with lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;189:832–44. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201309-1611OC. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fucikova J, Becht E, Iribarren K, Goc J, Remark R, Damotte D, Alifano M, Devi P, Biton J, Germain C, Lupo A, Fridman WH, Dieu-Nosjean M-C, et al. Calreticulin Expression in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers Correlates with Increased Accumulation of Antitumor Immune Cells and Favorable Prognosis. Cancer Res. 2016 doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1142. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

