Mitotic Checkpoint Regulators Control Insulin Signaling and Metabolic Homeostasis
- PMID: 27374329
- PMCID: PMC5560052
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.074
Mitotic Checkpoint Regulators Control Insulin Signaling and Metabolic Homeostasis
Abstract
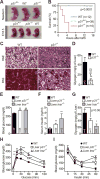
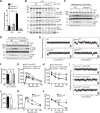
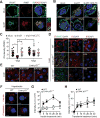
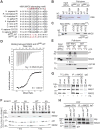
Insulin signaling regulates many facets of animal physiology. Its dysregulation causes diabetes and other metabolic disorders. The spindle checkpoint proteins MAD2 and BUBR1 prevent precocious chromosome segregation and suppress aneuploidy. The MAD2 inhibitory protein p31(comet) promotes checkpoint inactivation and timely chromosome segregation. Here, we show that whole-body p31(comet) knockout mice die soon after birth and have reduced hepatic glycogen. Liver-specific ablation of p31(comet) causes insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, glucose intolerance, and hyperglycemia and diminishes the plasma membrane localization of the insulin receptor (IR) in hepatocytes. MAD2 directly binds to IR and facilitates BUBR1-dependent recruitment of the clathrin adaptor AP2 to IR. p31(comet) blocks the MAD2-BUBR1 interaction and prevents spontaneous clathrin-mediated IR endocytosis. BUBR1 deficiency enhances insulin sensitivity in mice. BUBR1 depletion in hepatocytes or the expression of MAD2-binding-deficient IR suppresses the metabolic phenotypes of p31(comet) ablation. Our findings establish a major IR regulatory mechanism and link guardians of chromosome stability to nutrient metabolism.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
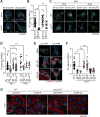
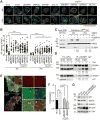
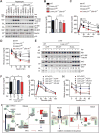
Comment in
-
Metabolism: MAD interactions with insulin receptor.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Jul 21;17(8):462-3. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.97. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27440312 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
p31comet-mediated extraction of Mad2 from the MCC promotes efficient mitotic exit.J Cell Sci. 2011 Nov 15;124(Pt 22):3905-16. doi: 10.1242/jcs.093286. Epub 2011 Nov 18. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 22100920 Free PMC article.
-
Mode of interaction of TRIP13 AAA-ATPase with the Mad2-binding protein p31comet and with mitotic checkpoint complexes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 15;112(37):11536-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1515358112. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26324890 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation regulates the p31Comet-mitotic arrest-deficient 2 (Mad2) interaction to promote spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) activity.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 18;289(16):11367-11373. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.520841. Epub 2014 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24596092 Free PMC article.
-
The Mad2-Binding Protein p31comet as a Potential Target for Human Cancer Therapy.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2021;21(5):401-415. doi: 10.2174/1568009621666210129095726. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2021. PMID: 33511944 Review.
-
Preventing aneuploidy: the contribution of mitotic checkpoint proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Sep;1786(1):24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2008.04.001. Epub 2008 Apr 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18472014 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolism: MAD interactions with insulin receptor.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Jul 21;17(8):462-3. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.97. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27440312 No abstract available.
-
Synergistic activation of the insulin receptor via two distinct sites.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2022 Apr;29(4):357-368. doi: 10.1038/s41594-022-00750-6. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35361965 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA profile in liver tissue of EpCAM knockout mice.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Sep;44(3):1063-1077. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4270. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31524221 Free PMC article.
-
Transient excited states of the metamorphic protein Mad2 and their implications for function.Proteins. 2025 Jan;93(1):302-319. doi: 10.1002/prot.26667. Epub 2024 Jan 14. Proteins. 2025. PMID: 38221646 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous Effects of Calorie Content and Nutritional Components Underlie Dietary Influence on Pancreatic Cancer Susceptibility.Cell Rep. 2020 Jul 14;32(2):107880. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107880. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32668252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker DJ, Jeganathan KB, Cameron JD, Thompson M, Juneja S, Kopecka A, Kumar R, Jenkins RB, de Groen PC, Roche P, et al. BubR1 insufficiency causes early onset of aging-associated phenotypes and infertility in mice. Nat Genet. 2004;36:744–749. - PubMed
-
- Bluher M, Kahn BB, Kahn CR. Extended longevity in mice lacking the insulin receptor in adipose tissue. Science. 2003;299:572–574. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

