Histone acetylation is involved in TCDD‑induced cleft palate formation in fetal mice
- PMID: 27279340
- PMCID: PMC4940082
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5348
Histone acetylation is involved in TCDD‑induced cleft palate formation in fetal mice
Abstract
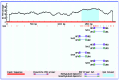
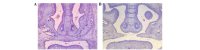
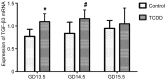
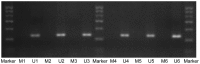
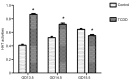
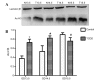
The aim of the present was to evaluate the effects of DNA methylation and histone acetylation on 2,3,7,8‑tetrachlorodibenzo‑p‑dioxin (TCDD)‑induced cleft palate in fetal mice. Pregnant mice (n=10) were randomly divided into two groups: i) TCDD group, mice were treated with 28 µg/kg TCDD on gestation day (GD) 10 by oral gavage; ii) control group, mice were treated with an equal volume of corn oil. On GD 16.5, the fetal mice were evaluated for the presence of a cleft palate. An additional 36 pregnant mice were divided into the control and TCDD groups, and palate samples were collected on GD 13.5, GD 14.5 and GD 15.5, respectively. Transforming growth factor‑β3 (TGF‑β3) mRNA expression, TGF‑β3 promoter methylation, histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity and histone H3 (H3) acetylation in the palates were evaluated in the two groups. The incidence of a cleft palate in the TCDD group was 93.55%, and no cases of cleft palate were identified in the control group. On GD 13.5 and GD 14.5, TGF‑β3 mRNA expression, HAT activity and acetylated H3 levels were significantly increased in the TCDD group compared with the control. Methylated bands were not observed in the TCDD or control groups. In conclusion, at the critical period of palate fusion (GD 13.5‑14.5), TCDD significantly increased TGF‑β3 gene expression, HAT activity and H3 acetylation. Therefore, histone acetylation may be involved in TCDD‑induced cleft palate formation in fetal mice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The role of histone H3 acetylation on cleft palate in mice induced by 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzopdioxin ].Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Sep;30(5):369-72. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25522490 Chinese.
-
[Mechanism of cleft palate in mice induced by 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin].Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011 Nov;27(6):448-53. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22292409 Chinese.
-
Alterations in DNA methyltransferases and methyl-CpG binding domain proteins during cleft palate formation as induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in mice.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Apr;17(4):5396-5401. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8521. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29393476
-
[Global DNA methylation changes during palatal formation in fetal mice induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlrodibenzo-p-dioxin].Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Sep;32(5):372-7. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 30066996 Chinese.
-
[The antagonistic effect of folic acid and resveratrol on cleft palate in mice induced by TCDD].Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013 May;29(3):197-201. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 25069347 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of Developmental Toxicity of Dioxins and Related Compounds.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 31;20(3):617. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030617. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30708991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocrine disrupting chemicals: gestational diabetes and beyond.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Apr 26;16(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01317-9. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38664841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of environmental exposures and human disease.Nat Rev Genet. 2023 May;24(5):332-344. doi: 10.1038/s41576-022-00569-3. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Nat Rev Genet. 2023. PMID: 36717624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin modifies alternative splicing in mouse liver.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 6;14(8):e0219747. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219747. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31386671 Free PMC article.
-
Multigenerational and Transgenerational Effects of Dioxins.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 17;20(12):2947. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122947. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31212893 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

