ATP6AP1 deficiency causes an immunodeficiency with hepatopathy, cognitive impairment and abnormal protein glycosylation
- PMID: 27231034
- PMCID: PMC4894975
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11600
ATP6AP1 deficiency causes an immunodeficiency with hepatopathy, cognitive impairment and abnormal protein glycosylation
Abstract
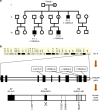
The V-ATPase is the main regulator of intra-organellar acidification. Assembly of this complex has extensively been studied in yeast, while limited knowledge exists for man. We identified 11 male patients with hemizygous missense mutations in ATP6AP1, encoding accessory protein Ac45 of the V-ATPase. Homology detection at the level of sequence profiles indicated Ac45 as the long-sought human homologue of yeast V-ATPase assembly factor Voa1. Processed wild-type Ac45, but not its disease mutants, restored V-ATPase-dependent growth in Voa1 mutant yeast. Patients display an immunodeficiency phenotype associated with hypogammaglobulinemia, hepatopathy and a spectrum of neurocognitive abnormalities. Ac45 in human brain is present as the common, processed ∼40-kDa form, while liver shows a 62-kDa intact protein, and B-cells a 50-kDa isoform. Our work unmasks Ac45 as the functional ortholog of yeast V-ATPase assembly factor Voa1 and reveals a novel link of tissue-specific V-ATPase assembly with immunoglobulin production and cognitive function.
Figures
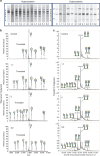
 represent predicted N-glycan structures, whereas the structures shown in black (
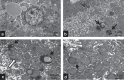
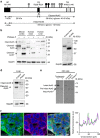
represent predicted N-glycan structures, whereas the structures shown in black ( ) are the experimentally confirmed glycans. (b) Western blot analysis of Ac45 in mouse cortex and in human brain and liver. Asterisk (*) indicates the deglycosylated form of cleaved-Ac45. Hash tags (#) indicate non-specific antibody reaction with PNGaseF present in the samples. (c) Western blot analysis of Ac45 in primary B cells from healthy controls in comparison with human liver. One of the two representative analyses is shown. (d) Western blot of Ac45 in liver tissue homogenates of control and patient 4.2. GapdH was used as loading control. (e) Analysis of newly synthesized Ac45 in immortalized human hepatocytes (IHH). Cells were transfected with Ac45 construct, pulsed for a 30-min period with 35S, and Ac45 was immunoprecipitated and analysed by SDS–PAGE. Cells were treated with or without tunicamycin during the 30-min pulse (left panel). Immunoprecipitated Ac45 protein was treated with or without Endo H or PNGaseF (right panel). Note during the 30-min pulse period, the presence of a minor portion of newly synthesized pre-intact-Ac45 protein is still in its unglycosylated proform and containing the signal peptide for translocation over the ER membrane. (f) IHH cells were stained with anti-Ac45 antibody (green) and antibodies against various organelle markers (magenta). Nuclear staining is shown in blue (DAPI). Co-localization is indicated by a white colour in the merged channel. The graph shows the fluorescent intensity profile along the cross-section indicated. Scale bar represents 10 μm. Staining for Sec31 is shown as example, other organelle markers are shown in Supplementary Fig. 5.
) are the experimentally confirmed glycans. (b) Western blot analysis of Ac45 in mouse cortex and in human brain and liver. Asterisk (*) indicates the deglycosylated form of cleaved-Ac45. Hash tags (#) indicate non-specific antibody reaction with PNGaseF present in the samples. (c) Western blot analysis of Ac45 in primary B cells from healthy controls in comparison with human liver. One of the two representative analyses is shown. (d) Western blot of Ac45 in liver tissue homogenates of control and patient 4.2. GapdH was used as loading control. (e) Analysis of newly synthesized Ac45 in immortalized human hepatocytes (IHH). Cells were transfected with Ac45 construct, pulsed for a 30-min period with 35S, and Ac45 was immunoprecipitated and analysed by SDS–PAGE. Cells were treated with or without tunicamycin during the 30-min pulse (left panel). Immunoprecipitated Ac45 protein was treated with or without Endo H or PNGaseF (right panel). Note during the 30-min pulse period, the presence of a minor portion of newly synthesized pre-intact-Ac45 protein is still in its unglycosylated proform and containing the signal peptide for translocation over the ER membrane. (f) IHH cells were stained with anti-Ac45 antibody (green) and antibodies against various organelle markers (magenta). Nuclear staining is shown in blue (DAPI). Co-localization is indicated by a white colour in the merged channel. The graph shows the fluorescent intensity profile along the cross-section indicated. Scale bar represents 10 μm. Staining for Sec31 is shown as example, other organelle markers are shown in Supplementary Fig. 5.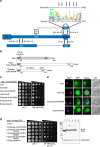
Similar articles
-
Severe phenotype of ATP6AP1-CDG in two siblings with a novel mutation leading to a differential tissue-specific ATP6AP1 protein pattern, cellular oxidative stress and hepatic copper accumulation.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2020 Jul;43(4):694-700. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12237. Epub 2020 Apr 7. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2020. PMID: 32216104 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in the X-linked ATP6AP2 cause a glycosylation disorder with autophagic defects.J Exp Med. 2017 Dec 4;214(12):3707-3729. doi: 10.1084/jem.20170453. Epub 2017 Nov 10. J Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 29127204 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of the vacuolar H+-ATPase accessory subunit Ac45 in Xenopus pituitary.Eur J Biochem. 1999 Jun;262(2):484-91. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00396.x. Eur J Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10336633
-
Novel insights into V-ATPase functioning: distinct roles for its accessory subunits ATP6AP1/Ac45 and ATP6AP2/(pro) renin receptor.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012 Mar;13(2):124-33. doi: 10.2174/138920312800493160. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 22044156 Review.
-
The cellular biology of proton-motive force generation by V-ATPases.J Exp Biol. 2000 Jan;203(Pt 1):89-95. doi: 10.1242/jeb.203.1.89. J Exp Biol. 2000. PMID: 10600677 Review.
Cited by
-
Congenital disorders of glycosylation: Prevalence, incidence and mutational spectrum in the Polish population.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2021 Feb 11;27:100726. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2021.100726. eCollection 2021 Jun. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2021. PMID: 33643843 Free PMC article.
-
Common variable immune deficiency: Dissection of the variable.Immunol Rev. 2019 Jan;287(1):145-161. doi: 10.1111/imr.12728. Immunol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30565247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic approaches in Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation (CDG) involving N-linked glycosylation: an update.Genet Med. 2020 Feb;22(2):268-279. doi: 10.1038/s41436-019-0647-2. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Genet Med. 2020. PMID: 31534212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The vacuolar-ATPase complex and assembly factors, TMEM199 and CCDC115, control HIF1α prolyl hydroxylation by regulating cellular iron levels.Elife. 2017 Mar 15;6:e22693. doi: 10.7554/eLife.22693. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28296633 Free PMC article.
-
What is new in CDG?J Inherit Metab Dis. 2017 Jul;40(4):569-586. doi: 10.1007/s10545-017-0050-6. Epub 2017 May 8. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2017. PMID: 28484880 Review.
References
-
- Schoonderwoert V. T. & Martens G. J. Proton pumping in the secretory pathway. J. Membr. Biol. 182, 159–169 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Karet F. E. et al.. Mutations in the gene encoding B1 subunit of H+-ATPase cause renal tubular acidosis with sensorineural deafness. Nat. Genet. 21, 84–90 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Smith A. N. et al.. Mutations in ATP6N1B, encoding a new kidney vacuolar proton pump 116-kD subunit, cause recessive distal renal tubular acidosis with preserved hearing. Nat. Genet. 26, 71–75 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

