A novel TRPV4-specific agonist inhibits monocyte adhesion and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 27191895
- PMCID: PMC5122337
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9376
A novel TRPV4-specific agonist inhibits monocyte adhesion and atherosclerosis
Abstract
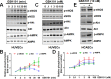
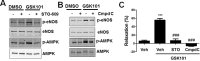
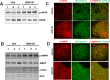
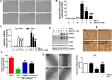
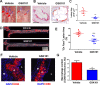
TRPV4 ion channel mediates vascular mechanosensitivity and vasodilation. Here, we sought to explore whether non-mechanical activation of TRPV4 could limit vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. We found that GSK1016790A, a potent and specific small-molecule agonist of TRPV4, induces the phosphorylation and activation of eNOS partially through the AMPK pathway. Moreover, GSK1016790A inhibited TNF-α-induced monocyte adhesion to human endothelial cells. Mice given GSK1016790A showed increased phosphorylation of eNOS and AMPK in the aorta and decreased leukocyte adhesion to TNF-α-inflamed endothelium. Importantly, oral administration of GSK1016790A reduced atherosclerotic plaque formation in ApoE deficient mice fed a Western-type diet. Together, the present study suggests that pharmacological activation of TRPV4 may serve as a potential therapeutic approach to treat atherosclerosis.
Keywords: AMPK; GSK1016790A; TRPV4; atherosclerosis; shear stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
N-((1S)-1-{[4-((2S)-2-{[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)sulfonyl]amino}-3-hydroxypropanoyl)-1-piperazinyl]carbonyl}-3-methylbutyl)-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxamide (GSK1016790A), a novel and potent transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 channel agonist induces urinary bladder contraction and hyperactivity: Part I.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 Aug;326(2):432-42. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.139295. Epub 2008 May 22. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008. PMID: 18499743
-
The anti-inflammatory vasostatin-2 attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice and inhibits monocyte/macrophage recruitment.Thromb Haemost. 2017 Jan 26;117(2):401-414. doi: 10.1160/TH16-06-0475. Epub 2016 Nov 10. Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 27831589
-
Systemic activation of the transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 4 channel causes endothelial failure and circulatory collapse: Part 2.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 Aug;326(2):443-52. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.134551. Epub 2008 May 22. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008. PMID: 18499744
-
TRPV4-mediated endothelial Ca2+ influx and vasodilation in response to shear stress.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):H466-76. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00854.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19966050 Free PMC article.
-
Cell adhesion molecules as pharmaceutical target in atherosclerosis.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2012 Feb;12(2):175-83. doi: 10.2174/138955712798995057. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22070689 Review.
Cited by
-
Fluid shear stress modulates endothelial inflammation by targeting LIMS2.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020 Dec;245(18):1656-1663. doi: 10.1177/1535370220943837. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020. PMID: 32752897 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Roles of TRPV4 in Macrophages: A Need for Unbiased Profiling.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 20;12:828115. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.828115. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35126384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of mechanosensitive channels/receptors in atherosclerosis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 May 1;322(5):C927-C938. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00396.2021. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35353635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and functional analysis of a biflavone as a novel inhibitor of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4-dependent atherogenic processes.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 14;11(1):8173. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87696-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33854174 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 in Vascular Function.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 26;8:677661. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.677661. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33981725 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Davignon J, Ganz P. Role of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2004;109:III27–32. - PubMed
-
- Berk BC. Atheroprotective signaling mechanisms activated by steady laminar flow in endothelial cells. Circulation. 2008;117:1082–1089. - PubMed
-
- Jin ZG, Ueba H, Tanimoto T, Lungu AO, Frame MD, Berk BC. Ligand-independent activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 by fluid shear stress regulates activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circ Res. 2003;93:354–363. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

