Discovery of unfixed endogenous retrovirus insertions in diverse human populations
- PMID: 27001843
- PMCID: PMC4843416
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1602336113
Discovery of unfixed endogenous retrovirus insertions in diverse human populations
Abstract
Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) have contributed to more than 8% of the human genome. The majority of these elements lack function due to accumulated mutations or internal recombination resulting in a solitary (solo) LTR, although members of one group of human ERVs (HERVs), HERV-K, were recently active with members that remain nearly intact, a subset of which is present as insertionally polymorphic loci that include approximately full-length (2-LTR) and solo-LTR alleles in addition to the unoccupied site. Several 2-LTR insertions have intact reading frames in some or all genes that are expressed as functional proteins. These properties reflect the activity of HERV-K and suggest the existence of additional unique loci within humans. We sought to determine the extent to which other polymorphic insertions are present in humans, using sequenced genomes from the 1000 Genomes Project and a subset of the Human Genome Diversity Project panel. We report analysis of a total of 36 nonreference polymorphic HERV-K proviruses, including 19 newly reported loci, with insertion frequencies ranging from <0.0005 to >0.75 that varied by population. Targeted screening of individual loci identified three new unfixed 2-LTR proviruses within our set, including an intact provirus present at Xq21.33 in some individuals, with the potential for retained infectivity.
Keywords: 1000 Genomes Project; HERV-K; HML-2; Human Genome Diversity Project; human endogenous retrovirus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
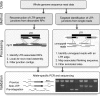





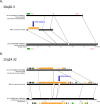
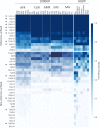
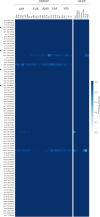



Comment in
-
HERV-K HML-2 diversity among humans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Apr 19;113(16):4240-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603569113. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27071126 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Human endogenous retrovirus K solo-LTR formation and insertional polymorphisms: implications for human and viral evolution.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Feb 10;101(6):1668-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307885100. Epub 2004 Feb 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14757818 Free PMC article.
-
Human endogenous retrovirus K106 (HERV-K106) was infectious after the emergence of anatomically modern humans.PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e20234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020234. Epub 2011 May 25. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21633511 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and association study with lung cancer for novel insertion polymorphisms of human endogenous retrovirus.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Nov;34(11):2531-8. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt253. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23872666 Clinical Trial.
-
Human Endogenous Retrovirus-K (HML-2)-Related Genetic Variation: Human Genome Diversity and Disease.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 28;14(12):2150. doi: 10.3390/genes14122150. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Control of Human Endogenous Retrovirus Expression: Focus on Regulation of Long-Terminal Repeats (LTRs).Viruses. 2017 May 31;9(6):130. doi: 10.3390/v9060130. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28561791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription of Endogenous Retroviruses: Broad and Precise Mechanisms of Control.Viruses. 2024 Aug 17;16(8):1312. doi: 10.3390/v16081312. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39205286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous Retroviruses Activity as a Molecular Signature of Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 30;20(23):6050. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236050. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31801288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repetitive elements in aging and neurodegeneration.Trends Genet. 2023 May;39(5):381-400. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2023.02.008. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Trends Genet. 2023. PMID: 36935218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retroviral Elements in Pathophysiology and as Therapeutic Targets for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Neurotherapeutics. 2022 Jul;19(4):1085-1101. doi: 10.1007/s13311-022-01233-8. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Neurotherapeutics. 2022. PMID: 35415778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole-Genome Analysis of Domestic Chicken Selection Lines Suggests Segregating Variation in ERV Makeups.Genes (Basel). 2019 Feb 20;10(2):162. doi: 10.3390/genes10020162. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30791656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boeke JD, Stoye JP. Retrotransposons, endogenous retroviruses, and the evolution of retroelements. In: Hughes S, Varmus H, editors. Retroviruses. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Plainview, NY: 1997. pp. 343–435. - PubMed
-
- McPherson JD, et al. International Human Genome Mapping Consortium A physical map of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409(6822):934–941. - PubMed
-
- Jern P, Coffin JM. Effects of retroviruses on host genome function. Annu Rev Genet. 2008;42:709–732. - PubMed
-
- Barbulescu M, et al. Many human endogenous retrovirus K (HERV-K) proviruses are unique to humans. Curr Biol. 1999;9(16):861–868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

