Matured hop extract reduces body fat in healthy overweight humans: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled parallel group study
- PMID: 26960416
- PMCID: PMC4784395
- DOI: 10.1186/s12937-016-0144-2
Matured hop extract reduces body fat in healthy overweight humans: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled parallel group study
Abstract
Background: Hops are the main components of beer that provide flavor and bitterness. Iso-α-acids, the bitter components of beer, have been reported to reduce body fat in humans, but the bitterness induced by effective doses of iso-α-acids precludes their acceptance as a nutrient. The matured hop bitter acids (MHBA) of oxidized hops appear to have a more pleasant bitterness compared to the sharper bitterness of iso-α-acids. While there has been little information concerning the identity of the MHBA compounds and their physiological effects, MHBA was recently found to be primarily composed of oxides derived from α-acids, and structurally similar to iso-α-acids. Here, we investigated the effects of matured hop extract (MHE) containing MHBA on reducing abdominal body fat in healthy subjects with a body mass index (BMI) of 25 to below 30 kg/m(2), classified as "obese level 1" in Japan or as "overweight" by the WHO.
Trial design: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled parallel group study.
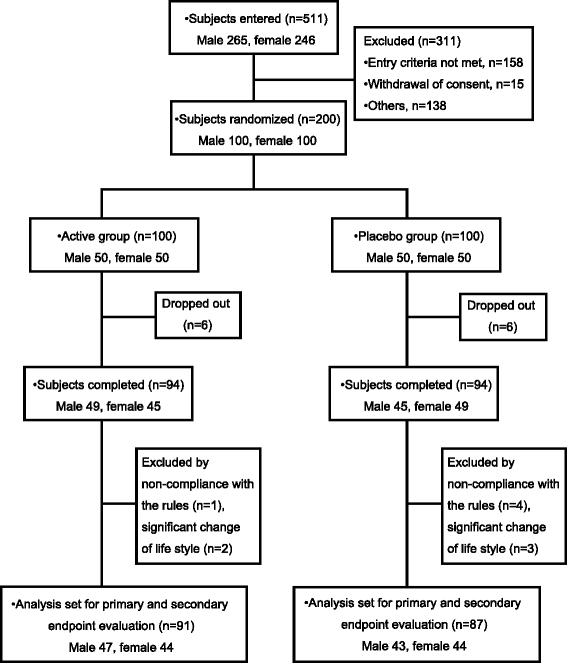
Methods: Two hundred subjects (male and female aged 20 to below 65 years with a BMI of 25 or more and less than 30 kg/m(2)) were randomly assigned to two groups. During a 12-week ingestion period, the subjects in each group ingested daily 350 mL of test-beverage, either containing MHE (with 35 mg MHBA), i.e. the namely active beverage, or a placebo beverage without MHE. The primary endpoint was reduction of the abdominal fat area as determined by CT scanning after continual ingestion of MHE for 12 weeks.
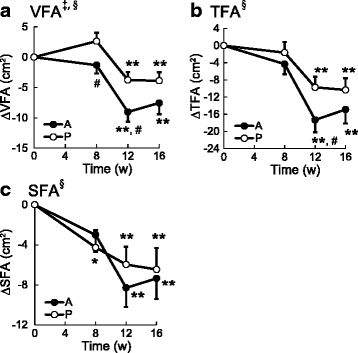
Results: Compared to the placebo group, a significant reduction was observed in the visceral fat area after 8 and 12 w, and in the total fat area after 12 w in the active group. There was also a concomitant decrease in body fat ratio in the active group compared to the placebo group. No adverse events related to the test beverages or clinically relevant abnormal changes in the circulatory, blood and urine parameters were observed in either group.
Conclusions: The present study suggests that continual ingestion of MHE safely reduces body fat, particularly the abdominal visceral fat of healthy overweight subjects.
Trial registration: UMIN-CTR UMIN000014185.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between the effect of matured hop extract and physical activity on reducing body fat: re-analysis of data from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled parallel group study.Nutr J. 2018 Oct 30;17(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12937-018-0405-3. Nutr J. 2018. PMID: 30376838 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Oral Paprika Xanthophyll Intake on Abdominal Fat in Healthy Overweight Humans: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study.J Oleo Sci. 2018 Sep 1;67(9):1149-1162. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess18076. Epub 2018 Aug 14. J Oleo Sci. 2018. PMID: 30111683 Clinical Trial.
-
Anthocyanin Rich-Black Soybean Testa Improved Visceral Fat and Plasma Lipid Profiles in Overweight/Obese Korean Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Med Food. 2016 Nov;19(11):995-1003. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2016.3762. Epub 2016 Nov 3. J Med Food. 2016. PMID: 27809637 Clinical Trial.
-
Improving Effects of Hop-Derived Bitter Acids in Beer on Cognitive Functions: A New Strategy for Vagus Nerve Stimulation.Biomolecules. 2020 Jan 13;10(1):131. doi: 10.3390/biom10010131. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 31940997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of tea catechin-rich beverages to reduce abdominal adiposity and metabolic syndrome risks in obese and overweight subjects: a pooled analysis of 6 human trials.Nutr Res. 2018 Jul;55:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2018.03.012. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Nutr Res. 2018. PMID: 29914623 Review.
Cited by
-
Could Natural Products Help in the Control of Obesity? Current Insights and Future Perspectives.Molecules. 2023 Sep 13;28(18):6604. doi: 10.3390/molecules28186604. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37764380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cinnamon and Hop Extracts as Potential Immunomodulators for Severe COVID-19 Cases.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Feb 26;12:589783. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.589783. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33719281 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effects of the Non-Alcoholic Fraction of Beer on Abdominal Fat, Osteoporosis, and Body Hydration in Women.Molecules. 2020 Aug 27;25(17):3910. doi: 10.3390/molecules25173910. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32867219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To beer or not to beer: A meta-analysis of the effects of beer consumption on cardiovascular health.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 3;15(6):e0233619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233619. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32492025 Free PMC article.
-
Supplementation with Matured Hop Bitter Acids Improves Cognitive Performance and Mood State in Healthy Older Adults with Subjective Cognitive Decline.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;76(1):387-398. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200229. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 32474473 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

