MicroRNA-410-5p as a potential serum biomarker for the diagnosis of prostate cancer
- PMID: 26900347
- PMCID: PMC4759854
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-016-0285-6
MicroRNA-410-5p as a potential serum biomarker for the diagnosis of prostate cancer
Abstract
Background: Prostate cancer (PCa) remains to be a diagnostic challenge due to its variable presentation and the lack of reliable diagnosis tool. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate gene in extensive range of pathophysiologic processes. Plasma miRNAs are ideal biomarkers in heart failure, diabetes and other disease. However, using circulating miRNAs as biomarkers for the diagnosis of PCa is still unknown.
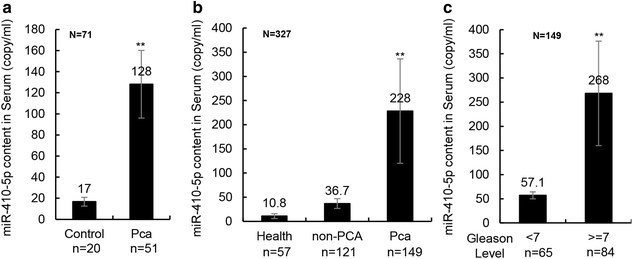
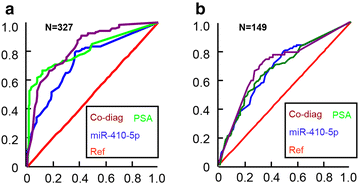
Methods: 149 PCa patients, 57 healthy controls, and 121 non-cancer patients (benign prostatic hyperplasia and other urinary diseases) were enrolled in this study. The reverse transcription of miRNA and SYBR-Green-based double standards curve miRNA quantitative polymerase chain reactions (qPCR) were used to evaluate the dysregulated miR-410-5p. Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of miR-410-5p identified as the alternative biomarker.
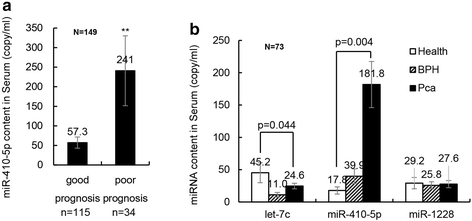
Results: Circulating miRNA-410-5p (miR-410-5p) level was significantly higher in the PCa patients than in healthy controls or non-cancer patients. ROC curve analysis showed that plasma miR-410-5p was a specific diagnostic biomarker of PCa with an area under curve(AUC) of 0.8097 (95 % confidence interval, 0.7371-0.8823; P < 0.001).
Conclusions: The serum miR-410-5p level is a potential biomarker for the diagnosis of PCa.
Keywords: Circulating miRNA; Diagnosis; Prostate cancer; miR-410-5p.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma microRNAs as potential new biomarkers for early detection of early gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Apr 7;25(13):1580-1591. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i13.1580. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30983818 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Value of Peripheral Blood miR-374b-5p in Patients with Prostate Cancer.Clin Lab. 2020 Jan 1;66(1). doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2019.190620. Clin Lab. 2020. PMID: 32013356
-
Circulating let-7f-5p improve risk prediction of prostate cancer in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia.J Cancer. 2020 May 18;11(15):4542-4549. doi: 10.7150/jca.45077. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32489471 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Metastasis-Related microRNAs in Prostate Cancer Progression and Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 6;13(17):4492. doi: 10.3390/cancers13174492. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34503302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Value of microRNA-375 as Future Biomarker for Prostate Cancer Detection: A Meta-Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Apr 10;58(4):529. doi: 10.3390/medicina58040529. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35454368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic value of strand-specific miRNA-101-3p and miRNA-101-5p for hepatocellular carcinoma and a bioinformatic analysis of their possible mechanism of action.FEBS Open Bio. 2017 Dec 20;8(1):64-84. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12349. eCollection 2018 Jan. FEBS Open Bio. 2017. PMID: 29321958 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Serum microRNA Expression Profiles and Comparison with Small Intestinal microRNA Expression Profiles in Weaned Piglets.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 15;11(9):e0162776. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162776. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27632531 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers That Differentiate Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia from Prostate Cancer: A Literature Review.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Jul 1;12:5225-5241. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S250829. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32669872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current advances of liquid biopsies in prostate cancer: Molecular biomarkers.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2023 Jul 19;30:27-38. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2023.07.004. eCollection 2023 Sep 21. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2023. PMID: 37575217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Electrochemical Advancements for Liquid-Biopsy Nucleic Acid Detection for Point-of-Care Prostate Cancer Diagnostics and Prognostics.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Sep 14;14(9):443. doi: 10.3390/bios14090443. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39329818 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tao ZQ, Shi AM, Wang KX, Zhang WD. Epidemiology of prostate cancer: current status. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(5):805–812. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

