Within-host evolution of bacterial pathogens
- PMID: 26806595
- PMCID: PMC5053366
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro.2015.13
Within-host evolution of bacterial pathogens
Abstract
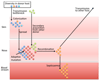
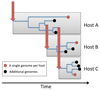
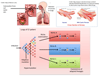
Whole-genome sequencing has opened the way for investigating the dynamics and genomic evolution of bacterial pathogens during the colonization and infection of humans. The application of this technology to the longitudinal study of adaptation in an infected host--in particular, the evolution of drug resistance and host adaptation in patients who are chronically infected with opportunistic pathogens--has revealed remarkable patterns of convergent evolution, suggestive of an inherent repeatability of evolution. In this Review, we describe how these studies have advanced our understanding of the mechanisms and principles of within-host genome evolution, and we consider the consequences of findings such as a potent adaptive potential for pathogenicity. Finally, we discuss the possibility that genomics may be used in the future to predict the clinical progression of bacterial infections and to suggest the best option for treatment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genomic perspectives on the evolution and spread of bacterial pathogens.Proc Biol Sci. 2015 Dec 22;282(1821):20150488. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2015.0488. Proc Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26702036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights from genomics into bacterial pathogen populations.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002874. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002874. Epub 2012 Sep 6. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22969423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial pathogen evolution: breaking news.Trends Genet. 2011 Jan;27(1):32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2010.10.001. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Trends Genet. 2011. PMID: 21047697 Review.
-
Functional characterization of the Mycobacterium abscessus genome coupled with condition specific transcriptomics reveals conserved molecular strategies for host adaptation and persistence.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 5;17:553. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2868-y. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27495169 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of Drug Resistance in Bacteria.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;915:49-67. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-32189-9_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27193537 Review.
Cited by
-
Within-Host Genotypic and Phenotypic Diversity of Contemporaneous Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from Blood Cultures of Patients with Bacteremia.mBio. 2022 Dec 20;13(6):e0290622. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02906-22. Epub 2022 Nov 29. mBio. 2022. PMID: 36445082 Free PMC article.
-
Intrahost Evolution of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 Among Individuals With Reoccurring Skin and Soft-Tissue Infections.J Infect Dis. 2016 Sep 15;214(6):895-905. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw242. Epub 2016 Jun 10. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27288537 Free PMC article.
-
Horizontally transmitted symbiont populations in deep-sea mussels are genetically isolated.ISME J. 2019 Dec;13(12):2954-2968. doi: 10.1038/s41396-019-0475-z. Epub 2019 Aug 8. ISME J. 2019. PMID: 31395952 Free PMC article.
-
Group B streptococcus virulence factors associated with different clinical syndromes: Asymptomatic carriage in pregnant women and early-onset disease in the newborn.Front Microbiol. 2023 Feb 13;14:1093288. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1093288. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36860481 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infections Using Molecular Methods.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Feb 12;11(2):239. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11020239. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35203841 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
Lieberman et al (2011) Nat Genet
- [Study of a B. dolosa outbreak in cystic fibrosis patients revealed evidence for adaptation to the host in the form of convergent evolution across multiple patients at genes encoding antibiotic resistance and bacterial membrane composition.]
-
-
-
Markussen et al (2014) mBio
- [Investigation of a 32-year persistent P. aeruginosa DK1 infection showed diversification and co-existence of sub-lineages with distinct functional and genomic signatures and rates of evolution that may occupy different niches within the cystic fibrosis airway.]
-
-
-
Marvig et al (2013) PLoS Genet
- [Evolutionary analysis of the P. aeruginosa DK2 lineage over 38 years identified pathoadaptive mutations occurring independently in multiple patients in genes relating to antibiotic resistance, cell envelope and regulatory functions.]
-
-
-
Elholm et al (2014) Genome Biol
- [First documented case of extensively drug resistant (XDR) M. tuberculosis strain evolved from a susceptible ancestor within a single patient. Resistance for most drugs evolved multiple times, with ultimately one lineage prevailing.]
-
-
-
Kennemann et al (2011) PNAS
- [Examination of five longitudinally sampled patients infected with H. pylori, detailing extensive mutation and recombination within individual hosts.]
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

