Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 Is Associated with Glomerular Filtration Rate Progression and Incidence of Chronic Kidney Disease in Two Community-Based Cohorts of Elderly Individuals
- PMID: 26648944
- PMCID: PMC4662300
- DOI: 10.1159/000435863
Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 Is Associated with Glomerular Filtration Rate Progression and Incidence of Chronic Kidney Disease in Two Community-Based Cohorts of Elderly Individuals
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to explore and validate the longitudinal associations between soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (sTNFR1), glomerular filtration rate (GFR) progression, and chronic kidney disease (CKD) incidence in two independent community-based cohorts of elderly individuals with prespecified subgroup analyses in individuals without prevalent diabetes.
Research design and methods: Two community-based cohorts of elderly individuals were used with 5-year follow-up data on estimated GFR: the Uppsala Longitudinal Study of Adult Men (ULSAM; n = 437 men; mean age: 78 years) and the Prospective Investigation of the Vasculature in Uppsala Seniors (PIVUS; n = 703; mean age: 70 years; 51% women). GFR categories were defined as ≥60, 30-60, and <30 ml/min/1.73 m(2).
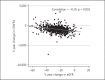
Results: In longitudinal multivariable logistic regression models adjusted for inflammatory markers and established cardiovascular risk factors, higher serum sTNFR1 was significantly associated with an increased risk to progress to a lower GFR category in both ULSAM and PIVUS [odds ratio (OR) per standard deviation (SD) increase 1.28 (95% CI 1.03-1.60) and OR 1.56 (95% CI 1.30-1.87), respectively]. Also, in subgroup analyses in individuals with a GFR ≥60 ml/min/1.73 m(2) at baseline, higher sTNFRs were associated with incident CKD after 5 years in both cohorts [ULSAM: OR per SD increase 1.49 (95% CI 1.16-1.9) and PIVUS: OR 1.84 (95% CI 1.50-2.26)]. Associations were similar in individuals without diabetes.
Conclusions: Higher circulating sTNFR1 independently predicts the progression to a worse GFR category and CKD incidence in elderly individuals even in the absence of diabetes. Further studies are warranted to investigate the underlying mechanisms, and to evaluate the clinical relevance of our findings.
Keywords: Albumin/creatinine ratio; Chronic kidney disease; Community; Glomerular filtration; Inflammation; TNF-α.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endostatin level is associated with kidney injury in the elderly: findings from two community-based cohorts.Am J Nephrol. 2014;40(5):417-24. doi: 10.1159/000369076. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Am J Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 25401956
-
Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (sTNFR1) is associated with increased total mortality due to cancer and cardiovascular causes - findings from two community based cohorts of elderly.Atherosclerosis. 2014 Nov;237(1):236-42. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.09.005. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Atherosclerosis. 2014. PMID: 25255422
-
Association between levels of pentraxin 3 and incidence of chronic kidney disease in the elderly.J Intern Med. 2016 Feb;279(2):173-9. doi: 10.1111/joim.12411. Epub 2015 Sep 9. J Intern Med. 2016. PMID: 26355706 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating cathepsin-S levels correlate with GFR decline and sTNFR1 and sTNFR2 levels in mice and humans.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 27;7:43538. doi: 10.1038/srep43538. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28240259 Free PMC article.
-
The association between glomerular filtration rate and left ventricular function in two independent community-based cohorts of elderly.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014 Nov;29(11):2069-74. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfu199. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014. PMID: 24916339 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Initial Validation of a Machine Learning-Derived Prognostic Test (KidneyIntelX) Integrating Biomarkers and Electronic Health Record Data To Predict Longitudinal Kidney Outcomes.Kidney360. 2020 Jun 30;1(8):731-739. doi: 10.34067/KID.0002252020. eCollection 2020 Aug 27. Kidney360. 2020. PMID: 35372952 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Papillary Necrosis (RPN) in an African Population: Disease Patterns, Relevant Pathways, and Management.Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 29;11(1):93. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11010093. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36672600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Found in Translation: Reasons for Optimism in the Pursuit to Prevent Chronic Kidney Disease After Acute Kidney Injury.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2019 Aug 16;6:2054358119868740. doi: 10.1177/2054358119868740. eCollection 2019. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 31452903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation of higher levels of soluble TNF-R1 with a shorter survival, independent of age, in recurrent glioblastoma.J Neurooncol. 2017 Feb;131(3):449-458. doi: 10.1007/s11060-016-2319-2. Epub 2016 Nov 17. J Neurooncol. 2017. PMID: 27858267 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment and Risk Prediction of Chronic Kidney Disease and Kidney Fibrosis Using Non-Invasive Biomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 26;25(7):3678. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073678. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612488 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pass HI, Mew D, Pass HA, Temeck BK. The macrophage, TNF, and other cytokines. Chest Surg Clin N Am. 1995;5:73–90. - PubMed
-
- Cabal-Hierro L, Lazo PS. Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor receptors. Cell Signal. 2012;24:1297–1305. - PubMed
-
- Carlsson AC, Juhlin CC, Larsson TE, Larsson A, Ingelsson E, Sundstrom J, Lind L, Arnlov J. Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (sTNFR1) is associated with increased total mortality due to cancer and cardiovascular causes – findings from two community based cohorts of elderly. Atherosclerosis. 2014;237:236–242. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources