Predictive assessment in pharmacogenetics of XRCC1 gene on clinical outcomes of advanced lung cancer patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy
- PMID: 26585370
- PMCID: PMC4653744
- DOI: 10.1038/srep16482
Predictive assessment in pharmacogenetics of XRCC1 gene on clinical outcomes of advanced lung cancer patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy
Abstract
Published data have shown inconsistent results about the pharmacogenetics of XRCC1 gene on clinical outcomes of advanced lung cancer patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. This meta-analysis aimed to summarize published findings and provide more reliable association. A total of 53 eligible studies including 7433 patients were included. Patients bearing the favorable TrpTrp and TrpArg genotypes of Arg194Trp were more likely to better response rates to platinum-based chemotherapy compared to those with the unfavorable ArgArg genotype (TrpTrp+TrpArg vs. ArgArg: odds ratio (OR) = 2.02, 95% CI, 1.66-2.45). The GlnGln and GlnArg genotypes of Arg399Gln were significantly associated with the poorer response rates compared to those with the ArgArg genotype (GlnGln +GlnArg vs. ArgArg: OR = 0.68, 95% CI, 0.54-0.86). The GlnGln genotype might be more closely associated with shorter survival time and higher risks of death for patients (GlnGln vs. ArgArg: hazard ratio (HR) = 1.14, 95% CI, 0.75-1.75). Our cumulative meta-analyses indicated a distinct apparent trend toward a better response rate for Arg194Trp, but a poorer response rate in Arg399Gln. These findings indicate a predictive role of XRCC1 polymorphisms in clinical outcomes. The use of XRCC1 polymorphisms as predictive factor of clinical outcomes in personalized chemotherapy treatment requires further verification from large well-designed pharmacogenetics studies.
Figures
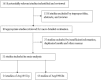
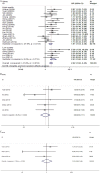

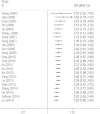
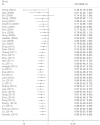
Similar articles
-
Association between the XRCC1 polymorphisms and clinical outcomes of advanced NSCLC treated with platinum-based chemotherapy: a meta-analysis based on the PRISMA statement.BMC Cancer. 2017 Jul 25;17(1):501. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3487-y. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28743242 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of polymorphisms in the XRCC1, XRCC3, and XPG genes on clinical outcomes of platinum-based chemotherapy for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Genet Mol Res. 2014 Mar 31;13(3):7617-25. doi: 10.4238/2014.March.31.13. Genet Mol Res. 2014. PMID: 24737519
-
Pharmacogenetic Association between XRCC1 Polymorphisms and Response to Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Asian Patients with NSCLC: A Meta-Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 22;2020:3520764. doi: 10.1155/2020/3520764. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33150172 Free PMC article.
-
Association between polymorphisms in XRCC1 gene and clinical outcomes of patients with lung cancer: a meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2012 Feb 17;12:71. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-71. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22339849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
XRCC1 Arg399Gln and clinical outcome of platinum-based treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis in 17 studies.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2012 Nov;13(11):875-83. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1200083. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2012. PMID: 23125080 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacogenomics of platinum-based chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: focusing on DNA repair systems.Med Oncol. 2017 Apr;34(4):48. doi: 10.1007/s12032-017-0905-6. Epub 2017 Feb 18. Med Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28215024 Review.
-
Genetic polymorphisms of GSTP1, XRCC1, XPC and ERCC1: prediction of clinical outcome of platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients of Bangladesh.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Sep;47(9):7073-7082. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05771-2. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32880833
-
An updated meta-analysis of 23 case-control studies on the association between miR-34b/c polymorphism and cancer risk.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 25;8(17):28888-28896. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16322. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28415817 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting DNA Damage Response in the Radio(Chemo)therapy of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 31;17(6):839. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060839. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27258253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Variants Associated With Response to Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Field Synopsis and Meta-Analysis.Br J Biomed Sci. 2024 Feb 21;81:11835. doi: 10.3389/bjbs.2024.11835. eCollection 2024. Br J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38450253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A. et al. Global cancer statistics. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 61, 69–90 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Parkin D. M., Bray F., Ferlay J. & Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 55, 74–108 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Spiro S. G. & Silvestri G. A. The treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine 11, 287–291 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

