Epstein-Barr Virus MicroRNA miR-BART20-5p Suppresses Lytic Induction by Inhibiting BAD-Mediated caspase-3-Dependent Apoptosis
- PMID: 26581978
- PMCID: PMC4719597
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02794-15
Epstein-Barr Virus MicroRNA miR-BART20-5p Suppresses Lytic Induction by Inhibiting BAD-Mediated caspase-3-Dependent Apoptosis
Abstract
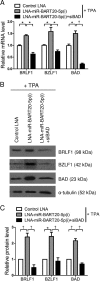
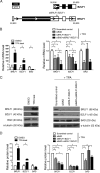
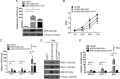
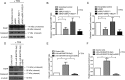
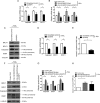
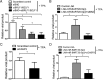
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a human gammaherpesvirus associated with a variety of tumor types. EBV can establish latency or undergo lytic replication in host cells. In general, EBV remains latent in tumors and expresses a limited repertoire of latent proteins to avoid host immune surveillance. When the lytic cycle is triggered by some as-yet-unknown form of stimulation, lytic gene expression and progeny virus production commence. Thus far, the exact mechanism of EBV latency maintenance and the in vivo triggering signal for lytic induction have yet to be elucidated. Previously, we have shown that the EBV microRNA miR-BART20-5p directly targets the immediate early genes BRLF1 and BZLF1 as well as Bcl-2-associated death promoter (BAD) in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma. In this study, we found that both mRNA and protein levels of BRLF1 and BZLF1 were suppressed in cells following BAD knockdown and increased after BAD overexpression. Progeny virus production was also downregulated by specific knockdown of BAD. Our results demonstrated that caspase-3-dependent apoptosis is a prerequisite for BAD-mediated EBV lytic cycle induction. Therefore, our data suggest that miR-BART20-5p plays an important role in latency maintenance and tumor persistence of EBV-associated gastric carcinoma by inhibiting BAD-mediated caspase-3-dependent apoptosis, which would trigger immediate early gene expression.
Importance: EBV has an ability to remain latent in host cells, including EBV-associated tumor cells hiding from immune surveillance. However, the exact molecular mechanisms of EBV latency maintenance remain poorly understood. Here, we demonstrated that miR-BART20-5p inhibited the expression of EBV immediate early genes indirectly, by suppressing BAD-induced caspase-3-dependent apoptosis, in addition to directly, as we previously reported. Our study suggests that EBV-associated tumor cells might endure apoptotic stress to some extent and remain latent with the aid of miR-BART20-5p. Blocking the expression or function of BART20-5p may expedite EBV-associated tumor cell death via immune attack and apoptosis.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA miR-BART20-5p stabilizes Epstein-Barr virus latency by directly targeting BZLF1 and BRLF1.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(16):9027-37. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00721-14. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24899173 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus miR-BART20-5p regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting BAD.Cancer Lett. 2015 Jan 28;356(2 Pt B):733-42. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.10.023. Epub 2014 Oct 24. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25449437
-
Cellular differentiation regulator BLIMP1 induces Epstein-Barr virus lytic reactivation in epithelial and B cells by activating transcription from both the R and Z promoters.J Virol. 2015 Feb;89(3):1731-43. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02781-14. Epub 2014 Nov 19. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25410866 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis of Epstein-Barr Virus Latency Establishment and Lytic Reactivation.Viruses. 2021 Nov 23;13(12):2344. doi: 10.3390/v13122344. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34960613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation and dysregulation of Epstein-Barr virus latency: implications for the development of autoimmune diseases.Autoimmunity. 2008 May;41(4):298-328. doi: 10.1080/08916930802024772. Autoimmunity. 2008. PMID: 18432410 Review.
Cited by
-
EBV miRNAs are potent effectors of tumor cell transcriptome remodeling in promoting immune escape.PLoS Pathog. 2021 May 6;17(5):e1009217. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009217. eCollection 2021 May. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33956915 Free PMC article.
-
B Cell Receptor Activation and Chemical Induction Trigger Caspase-Mediated Cleavage of PIAS1 to Facilitate Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation.Cell Rep. 2017 Dec 19;21(12):3445-3457. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.11.071. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 29262325 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs involve in tumorigenesis and development.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021 Mar 28;46(3):300-308. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2021.190744. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021. PMID: 33927078 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Viral miRNA regulation of host gene expression.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Sep 15;146:2-19. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.11.007. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36463091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging role of BAD and DAD1 as potential targets and biomarkers in cancer.Oncol Lett. 2021 Dec;22(6):811. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13072. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34671425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

