Targeting the ROR1 and ROR2 receptors in epithelial ovarian cancer inhibits cell migration and invasion
- PMID: 26515598
- PMCID: PMC4741897
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5643
Targeting the ROR1 and ROR2 receptors in epithelial ovarian cancer inhibits cell migration and invasion
Abstract
Aim: In recent years, the Wnt signalling pathway has been implicated in epithelial ovarian cancer and its members have potential as diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic targets. Here we investigated the role of two Wnt receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), ROR1 and ROR2, and their putative ligand, Wnt5a, in ovarian cancer.
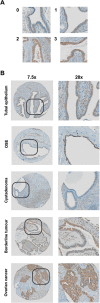
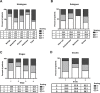
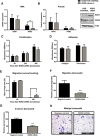
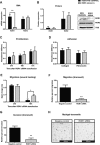
Methods: Immunohistochemistry for ROR2 was performed in a large patient cohort, including benign controls, borderline tumours and epithelial ovarian cancer. In addition, siRNA was used to silence ROR1, ROR2 and Wnt5a individually, and together, in two ovarian cancer cell lines, and the effects on cell proliferation, adhesion, migration and invasion were measured.
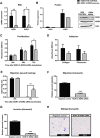
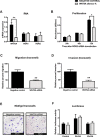
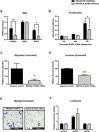
Results: ROR2 expression is significantly increased in ovarian cancer patients compared to patients with benign disease. In vitro assays showed that silencing either receptor inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration and invasion, and concurrently silencing both receptors has an even stronger inhibitory effect on proliferation, migration and invasion.
Conclusions: ROR2 expression is increased in epithelial ovarian cancer, and silencing ROR2 and its sister receptor ROR1 has a strong inhibitory effect on the ability of ovarian cancer cells to proliferate, migrate and invade through an extracellular matrix.
Keywords: ROR1; ROR2; Wnt signalling; epithelial ovarian cancer; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ROR1 and ROR2 play distinct and opposing roles in endometrial cancer.Gynecol Oncol. 2018 Mar;148(3):576-584. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2018.01.025. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Gynecol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29395309
-
Wnt5a induces ROR1/ROR2 heterooligomerization to enhance leukemia chemotaxis and proliferation.J Clin Invest. 2016 Feb;126(2):585-98. doi: 10.1172/JCI83535. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 26690702 Free PMC article.
-
Autonomous regulation of osteosarcoma cell invasiveness by Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling.Oncogene. 2009 Sep 10;28(36):3197-208. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.175. Epub 2009 Jun 29. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19561643
-
Insight into the role of Wnt5a-induced signaling in normal and cancer cells.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2015;314:117-48. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2014.10.003. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25619716 Review.
-
Role of the Ror family receptors in Wnt5a signaling.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024 May;60(5):489-501. doi: 10.1007/s11626-024-00885-4. Epub 2024 Apr 8. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024. PMID: 38587578 Review.
Cited by
-
Afatinib, an EGFR inhibitor, decreases EMT and tumorigenesis of Huh‑7 cells by regulating the ERK‑VEGF/MMP9 signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Oct;20(4):3317-3325. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10562. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31432165 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling proteome changes and potential regulatory proteins of bovine follicular Granulosa cells by mass spectrometry and multi-omics analysis.Proteome Sci. 2019 Oct 25;17:4. doi: 10.1186/s12953-019-0152-1. eCollection 2019. Proteome Sci. 2019. PMID: 31673248 Free PMC article.
-
Do patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma express receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1? Results of an observational study.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2021 Jan-Apr;25(1):105-109. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_293_18. Epub 2021 May 14. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34349419 Free PMC article.
-
The evolving roles of Wnt signaling in stem cell proliferation and differentiation, the development of human diseases, and therapeutic opportunities.Genes Dis. 2023 Jul 22;11(3):101026. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.04.042. eCollection 2024 May. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 38292186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WNT signaling inducing activity in ascites predicts poor outcome in ovarian cancer.Theranostics. 2020 Jan 1;10(2):537-552. doi: 10.7150/thno.37423. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 31903136 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tothill RW, Tinker AV, George J, Brown R, Fox SB, Lade S, Johnson DS, Trivett MK, Etemadmoghadam D, Locandro B, Traficante N, Fereday S, Hung JA, Chiew YE, Haviv I, Australian Ovarian Cancer Study G et al. Novel molecular subtypes of serous and endometrioid ovarian cancer linked to clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:5198–5208. - PubMed
-
- Tan TZ, Miow QH, Huang RY, Wong MK, Ye J, Lau JA, Wu MC, Bin Abdul Hadi LH, Soong R, Choolani M, Davidson B, Nesland JM, Wang LZ, Matsumura N, Mandai M, Konishi I, et al. Functional genomics identifies five distinct molecular subtypes with clinical relevance and pathways for growth control in epithelial ovarian cancer. EMBO molecular medicine. 2013;5:983–998. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ford CE, Punnia-Moorthy G, Henry CE, Llamosas E, Nixdorf S, Olivier J, Caduff R, Ward RL, Heinzelmann-Schwarz V. The non-canonical Wnt ligand, Wnt5a, is upregulated and associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecologic Oncology. 2014;134:338–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

