Modulation of Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling by Human Herpesvirus 8 Interferon Regulatory Factor 1
- PMID: 26512076
- PMCID: PMC4702585
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01903-15
Modulation of Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling by Human Herpesvirus 8 Interferon Regulatory Factor 1
Abstract
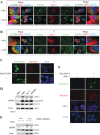
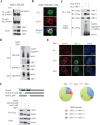
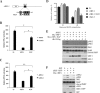
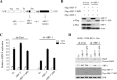
Mitochondrial lipid raft-like microdomains, experimentally also termed mitochondrial detergent-resistant membrane fractions (mDRM), play a role as platforms for recruiting signaling molecules involved in antiviral responses such as apoptosis and innate immunity. Viruses can modulate mitochondrial functions for their own survival and replication. However, viral regulation of the antiviral responses via mDRM remains incompletely understood. Here, we report that human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8) gene product viral interferon regulatory factor 1 (vIRF-1) is targeted to mDRM during virus replication and negatively regulates the mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS)-mediated antiviral responses. The N-terminal region of vIRF-1 interacts directly with membrane lipids, including cardiolipin. In addition, a GxRP motif within the N terminus of vIRF-1, conserved in the mDRM-targeting region of mitochondrial proteins, including PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1) and MAVS, was found to be important for vIRF-1 association with mitochondria. Furthermore, MAVS, which has the potential to promote vIRF-1 targeting to mDRM possibly by inducing cardiolipin exposure on the outer membrane of mitochondria, interacts with vIRF-1, which, in turn, inhibits MAVS-mediated antiviral signaling. Consistent with these results, vIRF-1 targeting to mDRM contributes to promotion of HHV-8 productive replication and inhibition of associated apoptosis. Combined, our results suggest novel molecular mechanisms for negative-feedback regulation of MAVS by vIRF-1 during virus replication.
Importance: Successful virus replication is in large part achieved by the ability of viruses to counteract apoptosis and innate immune responses elicited by infection of host cells. Recently, mitochondria have emerged to play a central role in antiviral signaling. In particular, mitochondrial lipid raft-like microdomains appear to function as platforms in cell apoptosis signaling. However, viral regulation of antiviral signaling through the mitochondrial microdomains remains incompletely understood. The present study demonstrates that HHV-8-encoded vIRF-1 targets to the mitochondrial detergent-resistant microdomains via direct interaction with cardiolipin and inhibits MAVS protein-mediated apoptosis and type I interferon gene expression in a negative-feedback manner, thus promoting HHV-8 productive replication. These results suggest that vIRF-1 is the first example of a viral protein to inhibit mitochondrial antiviral signaling through lipid raft-like microdomains.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
USP7-Dependent Regulation of TRAF Activation and Signaling by a Viral Interferon Regulatory Factor Homologue.J Virol. 2020 Jan 6;94(2):e01553-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01553-19. Print 2020 Jan 6. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31666375 Free PMC article.
-
Human Herpesvirus 8 Interferon Regulatory Factors 1 and 3 Mediate Replication and Latency Activities via Interactions with USP7 Deubiquitinase.J Virol. 2018 Mar 14;92(7):e02003-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02003-17. Print 2018 Apr 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29343584 Free PMC article.
-
Biologically significant interaction of human herpesvirus 8 viral interferon regulatory factor 4 with ubiquitin-specific protease 7.J Virol. 2024 Jun 13;98(6):e0025524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00255-24. Epub 2024 May 16. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38752725 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of MAVS Expression and Signaling Function in the Antiviral Innate Immune Response.Front Immunol. 2020 May 27;11:1030. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01030. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32536927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of MAVS regulation at the mitochondrial membrane.J Mol Biol. 2013 Dec 13;425(24):5009-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.10.007. Epub 2013 Oct 9. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24120683 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic viral infections in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS).J Transl Med. 2018 Oct 1;16(1):268. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1644-y. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30285773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SINE RNA of the imprinted miRNA clusters mediates constitutive type III interferon expression and antiviral protection in hemochorial placentas.Cell Host Microbe. 2023 Jul 12;31(7):1185-1199.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2023.05.018. Epub 2023 Jun 13. Cell Host Microbe. 2023. PMID: 37315561 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of NIX-mediated mitophagy by an interferon regulatory factor homologue of human herpesvirus.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 19;10(1):3203. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11164-2. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31324791 Free PMC article.
-
Operation of mitochondrial machinery in viral infection-induced immune responses.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Oct;156:348-356. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.08.044. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30172712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy-competent mitochondrial translation elongation factor TUFM inhibits caspase-8-mediated apoptosis.Cell Death Differ. 2022 Feb;29(2):451-464. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00868-y. Epub 2021 Sep 12. Cell Death Differ. 2022. PMID: 34511600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carbone A, Gloghini A. 2008. KSHV/HHV8-associated lymphomas. Br J Haematol 140:13–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

