Decreased MicroRNA-26a expression causes cisplatin resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 26492332
- PMCID: PMC4910912
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1095405
Decreased MicroRNA-26a expression causes cisplatin resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is the most common cancer that is caused by perturbation of regulatory pathways rather than dysfunction of a single gene. Cisplatin (CDDP; cis-diamminedichloroplatinum II) is the first member of a class of platinum-containing anti-cancer medication, which binds to DNA and triggers apoptosis. CDDP-based chemotherapy is used to treat various types of cancers. However, the efficacy of CDDP in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is limited by acquired drug resistance. MicroRNAs have recently emerged as key regulators of cancers, and miR-26a is one of down-regulated miRNAs in A549/CDDPres cell line. This study aimed to investigate the role of miR-26a in CDDP resistance in NSCLC as well as the underlying mechanisms.
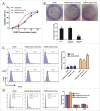
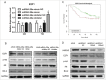
Methods: In this study, we analyzed expressional profiles of CDDP resistance-related mRNA, miRNA, and transcription factors (TF) that regulate miRNA expression in NSCLC. A549 cells were treated with CDDP, miR-26a mimic, or miR-26a inhibitor, and followed by biological analysis including drug sensitivity assay, colony formation assay, terminal-deoxynucleoitidyl Transferase Mediated Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) assay, and cell cycle analysis. Luciferase assay was used to determine the target of miR-26a. The regulation of miR-26a in Akt pathway was measured by western blot.
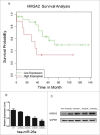
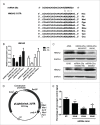
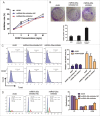
Results: High mobility group A (HMGA) 2 was identified as the target of miR-26a. Overexpression of miR-26a in A549 cells inhibited G1-S transition, increased cell death in response to CDDP treatment, and decreased the colony formation of A549 cells. MiR-26a significantly decreased the expression of E2F1, diminished Akt phosphorylation, and downregulated Bcl2 expression. Cell growth was suppressed by inhibiting HMGA2-mediated E2F1-Akt pathway.
Conclusion: MiR-26a is responsible for A549 cell sensitivity in the treatment of CDDP through regulating HMGA2-mediated E2F1-Akt pathway.
Keywords: Cisplatin resistance; E2F1; HMGA2; miR-26a; non-small-cell lung cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-181a and miR-630 regulate cisplatin-induced cancer cell death.Cancer Res. 2010 Mar 1;70(5):1793-803. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3112. Epub 2010 Feb 9. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20145152
-
miR-148b reverses cisplatin-resistance in non-small cell cancer cells via negatively regulating DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1(DNMT1) expression.J Transl Med. 2015 Apr 28;13:132. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0488-y. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25927928 Free PMC article.
-
EHD1 confers resistance to cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating intracellular cisplatin concentrations.BMC Cancer. 2016 Jul 13;16:470. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2527-3. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27411790 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as Regulators of Cisplatin Resistance in Lung Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(5):1869-80. doi: 10.1159/000438548. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26584286 Review.
-
MicroRNAs as the pivotal regulators of cisplatin resistance in osteosarcoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Sep;249:154743. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154743. Epub 2023 Aug 6. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37549518 Review.
Cited by
-
Application and Prospect of CRISPR/Cas9 Technology in Reversing Drug Resistance of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 10;13:900825. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.900825. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35620280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-1269b Drives Cisplatin Resistance of Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Modulating the PTEN/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jan 7;13:109-118. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S225010. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32021259 Free PMC article.
-
High Mobility Group A (HMGA): Chromatin Nodes Controlled by a Knotty miRNA Network.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 22;21(3):717. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030717. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31979076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney is associated with CDKN2A deletion and SLC family gene up-regulation.Oncotarget. 2016 May 24;7(21):29901-15. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9093. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27144525 Free PMC article.
-
[MicroRNA-26a and Tumor].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017 Nov 20;20(11):769-774. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2017.11.08. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29167007 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 2013; 63:11-30; PMID:23335087; http://dx.doi.org/10.3322/caac.21166 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Seve P, Reiman T, Dumontet C. The role of betaIII tubulin in predicting chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2010; 67:136-43; PMID:19828208; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.09.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Siddik ZH. Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene 2003; 22:7265-79; PMID:14576837; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206933 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xiao X, Yu S, Li S, Wu J, Ma R, Cao H, Zhu Y, Feng J. Exosomes: decreased sensitivity of lung cancer A549 cells to cisplatin. PloS one 2014; 9:e89534; PMID:24586853; http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089534 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stewart DJ. Mechanisms of resistance to cisplatin and carboplatin. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2007; 63:12-31; PMID:17336087; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2007.02.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
