A KSHV microRNA Directly Targets G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 to Promote the Migration and Invasion of Endothelial Cells by Inducing CXCR2 and Activating AKT Signaling
- PMID: 26402907
- PMCID: PMC4581863
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005171
A KSHV microRNA Directly Targets G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 to Promote the Migration and Invasion of Endothelial Cells by Inducing CXCR2 and Activating AKT Signaling
Abstract
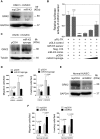
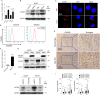
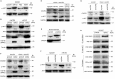
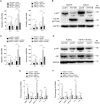
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is a highly disseminated angiogenic tumor of endothelial cells linked to infection by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV). KSHV encodes more than two dozens of miRNAs but their roles in KSHV-induced tumor dissemination and metastasis remain unknown. Here, we found that ectopic expression of miR-K12-3 (miR-K3) promoted endothelial cell migration and invasion. Bioinformatics and luciferase reporter analyses showed that miR-K3 directly targeted G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) kinase 2 (GRK2, official gene symbol ADRBK1). Importantly, overexpression of GRK2 reversed miR-K3 induction of cell migration and invasion. Furthermore, the chemokine receptor CXCR2, which was negatively regulated by GRK2, was upregulated in miR-K3-transduced endothelial cells. Knock down of CXCR2 abolished miR-K3-induced cell migration and invasion. Moreover, miR-K3 downregulation of GRK2 relieved its direct inhibitory effect on AKT. Both CXCR2 induction and the release of AKT from GRK2 were required for miR-K3 maximum activation of AKT and induction of cell migration and invasion. Finally, deletion of miR-K3 from the KSHV genome abrogated its effect on the GRK2/CXCR2/AKT pathway and KSHV-induced migration and invasion. Our data provide the first-line evidence that, by repressing GRK2, miR-K3 facilitates cell migration and invasion via activation of CXCR2/AKT signaling, which likely contribute to the dissemination of KSHV-induced tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The SH3BGR/STAT3 Pathway Regulates Cell Migration and Angiogenesis Induced by a Gammaherpesvirus MicroRNA.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Apr 29;12(4):e1005605. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005605. eCollection 2016 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27128969 Free PMC article.
-
A KSHV microRNA enhances viral latency and induces angiogenesis by targeting GRK2 to activate the CXCR2/AKT pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 May 31;7(22):32286-305. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8591. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27058419 Free PMC article.
-
A viral microRNA downregulates metastasis suppressor CD82 and induces cell invasion and angiogenesis by activating the c-Met signaling.Oncogene. 2017 Sep 21;36(38):5407-5420. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.139. Epub 2017 May 22. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28534512 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV microRNAs: Tricks of the Devil.Trends Microbiol. 2017 Aug;25(8):648-661. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.02.002. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Trends Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28259385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNAs and their roles in KSHV pathogenesis.Virus Res. 2019 Jun;266:15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2019.03.024. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Virus Res. 2019. PMID: 30951791 Review.
Cited by
-
Sperm associated antigen 9 promotes oncogenic KSHV-encoded interferon regulatory factor-induced cellular transformation and angiogenesis by activating the JNK/VEGFA pathway.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Aug 10;16(8):e1008730. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008730. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32776977 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV) microRNA K12-1 functions as an oncogene by activating NF-κB/IL-6/STAT3 signaling.Oncotarget. 2016 May 31;7(22):33363-73. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9221. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27166260 Free PMC article.
-
The expanding GRK interactome: Implications in cardiovascular disease and potential for therapeutic development.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Aug;110:52-64. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.05.008. Epub 2016 May 12. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27180008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-4638-5p inhibits castration resistance of prostate cancer through repressing Kidins220 expression and PI3K/AKT pathway activity.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):47444-47464. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10165. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27329728 Free PMC article.
-
The SH3BGR/STAT3 Pathway Regulates Cell Migration and Angiogenesis Induced by a Gammaherpesvirus MicroRNA.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Apr 29;12(4):e1005605. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005605. eCollection 2016 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27128969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, Lee F, Culpepper J, et al. (1994) Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Science 266: 1865–1869. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore PS, Said JW, Knowles DM (1995) Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N Engl J Med 332: 1186–1191. - PubMed
-
- Soulier J, Grollet L, Oksenhendler E, Cacoub P, Cazals-Hatem D, et al. (1995) Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman's disease. Blood 86: 1276–1280. - PubMed
-
- Ganem D (1997) KSHV and Kaposi's sarcoma: the end of the beginning? Cell 91: 157–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

