Clinical development of galunisertib (LY2157299 monohydrate), a small molecule inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway
- PMID: 26309397
- PMCID: PMC4539082
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S86621
Clinical development of galunisertib (LY2157299 monohydrate), a small molecule inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway
Abstract
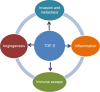
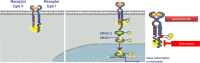
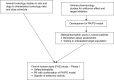
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling regulates a wide range of biological processes. TGF-β plays an important role in tumorigenesis and contributes to the hallmarks of cancer, including tumor proliferation, invasion and metastasis, inflammation, angiogenesis, and escape of immune surveillance. There are several pharmacological approaches to block TGF-β signaling, such as monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, antisense oligonucleotides, and small molecule inhibitors. Galunisertib (LY2157299 monohydrate) is an oral small molecule inhibitor of the TGF-β receptor I kinase that specifically downregulates the phosphorylation of SMAD2, abrogating activation of the canonical pathway. Furthermore, galunisertib has antitumor activity in tumor-bearing animal models such as breast, colon, lung cancers, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Continuous long-term exposure to galunisertib caused cardiac toxicities in animals requiring adoption of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic-based dosing strategy to allow further development. The use of such a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model defined a therapeutic window with an appropriate safety profile that enabled the clinical investigation of galunisertib. These efforts resulted in an intermittent dosing regimen (14 days on/14 days off, on a 28-day cycle) of galunisertib for all ongoing trials. Galunisertib is being investigated either as monotherapy or in combination with standard antitumor regimens (including nivolumab) in patients with cancer with high unmet medical needs such as glioblastoma, pancreatic cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma. The present review summarizes the past and current experiences with different pharmacological treatments that enabled galunisertib to be investigated in patients.
Keywords: ALK5; LY2157299; TGF-β; TGF-βRI kinase inhibitor; cancer; clinical trials; galunisertib.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiac Safety of TGF-β Receptor I Kinase Inhibitor LY2157299 Monohydrate in Cancer Patients in a First-in-Human Dose Study.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2015 Oct;15(4):309-23. doi: 10.1007/s12012-014-9297-4. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25488804 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase 1 study of galunisertib, a TGF-beta receptor I kinase inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015 Dec;76(6):1143-52. doi: 10.1007/s00280-015-2895-4. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26526984 Clinical Trial.
-
Galunisertib (LY2157299), a transforming growth factor-β receptor I kinase inhibitor, attenuates acute pancreatitis in rats.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2016 Aug 8;49(9):e5388. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20165388. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2016. PMID: 27509307 Free PMC article.
-
Tgf-beta type I receptor (Alk5) kinase inhibitors in oncology.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011 Dec;12(12):2190-202. doi: 10.2174/138920111798808257. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21619541 Review.
-
Lenvatinib: Role in thyroid cancer and other solid tumors.Cancer Treat Rev. 2016 Jan;42:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.11.003. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016. PMID: 26678514 Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in COPD induced by cigarette smoke: an update.Respir Res. 2022 Aug 31;23(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02153-z. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 36045410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome and proteome characterization of surface ectoderm cells differentiated from human iPSCs.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 23;6:32007. doi: 10.1038/srep32007. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27550649 Free PMC article.
-
Silence of Hippo Pathway Associates with Pro-Tumoral Immunosuppression: Potential Therapeutic Target of Glioblastomas.Cells. 2020 Jul 23;9(8):1761. doi: 10.3390/cells9081761. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32717825 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer prevention by short-term inhibition of TGFβ signaling.Nat Commun. 2022 Dec 7;13(1):7558. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35043-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36476730 Free PMC article.
-
Oncofetal reprogramming in tumor development and progression: novel insights into cancer therapy.MedComm (2020). 2023 Dec 2;4(6):e427. doi: 10.1002/mco2.427. eCollection 2023 Dec. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 38045829 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Piek E, Heldin CH, Ten Dijke P. Specificity, diversity, and regulation in TGF-beta superfamily signaling. FASEB J. 1999;13(15):2105–2124. - PubMed
-
- Anzano MA, Roberts AB, Meyers CA, et al. Synergistic interaction of two classes of transforming growth factors from murine sarcoma cells. Cancer Res. 1982;42(11):4776–4778. - PubMed
-
- Massague J, Blain SW, Lo RS. TGFbeta signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell. 2000;103(2):295–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

