Widespread Co-translational RNA Decay Reveals Ribosome Dynamics
- PMID: 26046441
- PMCID: PMC4461875
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.008
Widespread Co-translational RNA Decay Reveals Ribosome Dynamics
Abstract
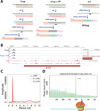
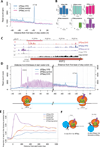
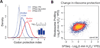
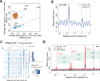
It is generally assumed that mRNAs undergoing translation are protected from decay. Here, we show that mRNAs are, in fact, co-translationally degraded. This is a widespread and conserved process affecting most genes, where 5'-3' transcript degradation follows the last translating ribosome, producing an in vivo ribosomal footprint. By sequencing the ends of 5' phosphorylated mRNA degradation intermediates, we obtain a genome-wide drug-free measurement of ribosome dynamics. We identify general translation termination pauses in both normal and stress conditions. In addition, we describe novel codon-specific ribosomal pausing sites in response to oxidative stress that are dependent on the RNase Rny1. Our approach is simple and straightforward and does not require the use of translational inhibitors or in vitro RNA footprinting that can alter ribosome protection patterns.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Dying mRNA Tells a Story of Its Life.Cell. 2015 Jun 4;161(6):1246-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.043. Cell. 2015. PMID: 26046434
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide quantification of 5'-phosphorylated mRNA degradation intermediates for analysis of ribosome dynamics.Nat Protoc. 2016 Feb;11(2):359-76. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.026. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Nat Protoc. 2016. PMID: 26820793 Free PMC article.
-
Translation complex profile sequencing to study the in vivo dynamics of mRNA-ribosome interactions during translation initiation, elongation and termination.Nat Protoc. 2017 Apr;12(4):697-731. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.189. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Nat Protoc. 2017. PMID: 28253237
-
The Ccr4-Not complex monitors the translating ribosome for codon optimality.Science. 2020 Apr 17;368(6488):eaay6912. doi: 10.1126/science.aay6912. Science. 2020. PMID: 32299921 Free PMC article.
-
Dual functions of ribosome recycling factor in protein biosynthesis: disassembling the termination complex and preventing translational errors.Biochimie. 1996;78(11-12):959-69. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(97)86718-1. Biochimie. 1996. PMID: 9150873 Review.
-
Ribosome structure and dynamics during translocation and termination.Annu Rev Biophys. 2010;39:227-44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.37.032807.125954. Annu Rev Biophys. 2010. PMID: 20192776 Review.
Cited by
-
Human DDX6 regulates translation and decay of inefficiently translated mRNAs.Elife. 2024 Jul 11;13:RP92426. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92426. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38989862 Free PMC article.
-
A Coding Sequence-Embedded Principle Governs Translational Reading Frame Fidelity.Research (Wash D C). 2018 Sep 20;2018:7089174. doi: 10.1155/2018/7089174. eCollection 2018. Research (Wash D C). 2018. PMID: 31549036 Free PMC article.
-
A short translational ramp determines the efficiency of protein synthesis.Nat Commun. 2019 Dec 18;10(1):5774. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13810-1. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31852903 Free PMC article.
-
Translational regulation in response to stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Yeast. 2019 Jan;36(1):5-21. doi: 10.1002/yea.3349. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Yeast. 2019. PMID: 30019452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Lsm1-7/Pat1 complex binds to stress-activated mRNAs and modulates the response to hyperosmotic shock.PLoS Genet. 2018 Jul 30;14(7):e1007563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007563. eCollection 2018 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30059503 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

