Prognostic Value and Clinicopathology Significance of MicroRNA-200c Expression in Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26035744
- PMCID: PMC4452703
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128642
Prognostic Value and Clinicopathology Significance of MicroRNA-200c Expression in Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
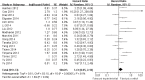
MiR-200c has been shown to be related to cancer formation and progression. However, the prognostic and clinicopathologic significance of miR-200c expression in cancer remain inconclusive. We carried out this systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the prognostic value of miR-200c expression in cancer. Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) of miR-200c for overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were calculated to measure the effective value of miR-200c expression on prognosis. The association between miR-200c expression and clinical significance was measured by odds ratios (ORs). Twenty-three studies were included in our meta-analysis. We found that miR-200c was not significantly correlated with OS (HR = 1.41, 95%Cl: 0.95-2.10; P = 0.09) and PFS (HR = 1.12, 95%Cl: 0.68-1.84; P = 0.67) in cancer. In our subgroup analysis, higher expression of miR-200c was significantly associated with poor OS in blood (HR = 2.10, 95%CI: 1.52-2.90, P<0.00001). Moreover, in clinicopathology analysis, miR-200c expression in blood was significantly associated with TNM stage, lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis. MiR-200c may have the potential to become a new blood biomarker to monitor cancer prognosis and progression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prognostic role of tissue and circulating microRNA-200c in malignant tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(3):1188-200. doi: 10.1159/000373943. Epub 2015 Feb 10. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25766530 Review.
-
Prognostic Role of MicroRNA-200c-141 Cluster in Various Human Solid Malignant Neoplasms.Dis Markers. 2015;2015:935626. doi: 10.1155/2015/935626. Epub 2015 Oct 18. Dis Markers. 2015. PMID: 26556949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum miR-200c is a novel prognostic and metastasis-predictive biomarker in patients with colorectal cancer.Ann Surg. 2014 Apr;259(4):735-43. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182a6909d. Ann Surg. 2014. PMID: 23982750 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating miR-200c as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer.J Transl Med. 2012 Sep 6;10:186. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-186. J Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22954417 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of MicroRNA-153 in human cancers: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 13;99(46):e22833. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022833. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33181653 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Role of the MicroRNA-200 Family in Various Carcinomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:1928021. doi: 10.1155/2017/1928021. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28321402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating mRNAs and miRNAs as candidate markers for the diagnosis and prognosis of prostate cancer.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 14;12(9):e0184094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184094. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28910345 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathologic significance of SIRT1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 22;8(32):52357-52365. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14096. eCollection 2017 Aug 8. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 28881735 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of microRNA-150 in various carcinomas: a meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Mar 11;9:1371-9. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S97969. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27042106 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kuschel B, Auranen A, McBride S, Novik KL, Antoniou A, Lipscombe JM, et al. (2002) Variants in DNA double-strand break repair genes and breast cancer susceptibility. Hum Mol Genet 11: 1399–1407. - PubMed
-
- Dai J, Tang K, Xiao W, Yu G, Zeng J, Li W, et al. (2014) Prognostic significance of C-reactive protein in urological cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15: 3369–3375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

