IκBβ enhances the generation of the low-affinity NFκB/RelA homodimer
- PMID: 25946967
- PMCID: PMC4425231
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8068
IκBβ enhances the generation of the low-affinity NFκB/RelA homodimer
Abstract
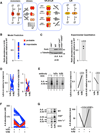
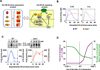
The NFκB family of dimeric transcription factors regulate inflammatory and immune responses. While the dynamic control of NFκB dimer activity via the IκB-NFκB signalling module is well understood, there is little information on how specific dimer repertoires are generated from Rel family polypeptides. Here we report the iterative construction-guided by in vitro and in vivo experimentation-of a mathematical model of the Rel-NFκB generation module. Our study reveals that IκBβ has essential functions within the Rel-NFκB generation module, specifically for the RelA:RelA homodimer, which controls a subset of NFκB target genes. Our findings revise the current dogma of the three classical, functionally related IκB proteins by distinguishing between a positive 'licensing' factor (IκBβ) that contributes to determining the available NFκB dimer repertoire in a cell's steady state, and negative feedback regulators (IκBα and -ɛ) that determine the duration and dynamics of the cellular response to an inflammatory stimulus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
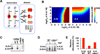
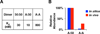
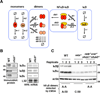
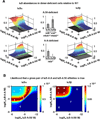
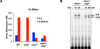
Similar articles
-
The nuclear factor kappa-B signaling pathway participates in dysregulation of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro and in human atherosclerosis.J Biol Chem. 1997 Jun 20;272(25):15817-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.25.15817. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9188479
-
p65 controls NF-κB activity by regulating cellular localization of IκBβ.Biochem J. 2011 Mar 1;434(2):253-63. doi: 10.1042/BJ20101220. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21158742
-
Exclusivity and Compensation in NFκB Dimer Distributions and IκB Inhibition.Biochemistry. 2019 May 28;58(21):2555-2563. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00008. Epub 2019 May 14. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31033276 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory logic of the NF-kappaB signaling system.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Jan;2(1):a000216. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000216. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20182598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A structural guide to proteins of the NF-kappaB signaling module.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009 Sep;1(3):a000075. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000075. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009. PMID: 20066103 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An epithelial Nfkb2 pathway exacerbates intestinal inflammation by supplementing latent RelA dimers to the canonical NF-κB module.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jun 22;118(25):e2024828118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2024828118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34155144 Free PMC article.
-
DNA and IκBα Both Induce Long-Range Conformational Changes in NFκB.J Mol Biol. 2017 Apr 7;429(7):999-1008. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.02.017. Epub 2017 Feb 27. J Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28249778 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and NF-κB Signaling in Prostate Cancer: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications.Cells. 2018 Aug 29;7(9):122. doi: 10.3390/cells7090122. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30158439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transient interactions modulate the affinity of NF-κB transcription factors for DNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jun 4;121(23):e2405555121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2405555121. Epub 2024 May 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38805268 Free PMC article.
-
The NF-κB multidimer system model: A knowledge base to explore diverse biological contexts.Sci Signal. 2023 Mar 14;16(776):eabo2838. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abo2838. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Sci Signal. 2023. PMID: 36917644 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

