Oral delivery of wafers made from HBsAg-expressing maize germ induces long-term immunological systemic and mucosal responses
- PMID: 25944300
- PMCID: PMC4445721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.04.080
Oral delivery of wafers made from HBsAg-expressing maize germ induces long-term immunological systemic and mucosal responses
Abstract
Background: The hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) has been administered over the last 20 years as a parenteral vaccine against the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Despite high seroconversion rates, chronic infection rates are still high worldwide. Orally delivered vaccines provide a practical alternative to injected vaccines, potentially helping poorly responding populations and providing a viable alternative for populations in remote locations. Anamnestic responses are vital to establishing the efficacy of a given vaccine and have been assessed in this study using a plant-based oral delivery platform expressing HBsAg.
Methods: Long-term immunological memory was assessed in mice injected with a primary dose of Recombivax and boosted with orally-delivered HBsAg wafers, control wafers, or parenterally-delivered commercial vaccine (Recombivax).
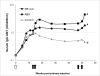
Results: Mice boosted with HBsAg orally-administered wafers displayed sharp increases in mucosal IgA titers in fecal material and steep increases in serum IgA, whereas mice boosted with Recombivax showed no detectable levels of IgA in either fecal or serum samples following four boosting treatments. Long-term memory in the orally-treated mice was evidenced by sustained fecal IgA, and serum IgA, IgG, and mIU/mL over one year, while Recombivax-treated mice displayed sustained serum IgG and mIU/mL. Furthermore, sharp increases in these same antibodies were induced after re-boosting at 47 and 50 weeks post-primary injection.
Conclusions: Orally-delivered vaccines can provide long-term immune responses mucosally and systemically. For sexually-transmitted diseases that can be acquired at mucosal surfaces, such as HBV, an oral delivery platform may provide added protection over a conventional parenterally administered vaccine.
Keywords: Anamnestic response; Bioencapsulation; Immunogenicity; Long-term immune memory; Maize oral vaccine; Mucosal; Plant vaccine; Subunit vaccine; Supercritical fluid extraction.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Supercritical fluid extraction provides an enhancement to the immune response for orally-delivered hepatitis B surface antigen.Vaccine. 2014 Mar 5;32(11):1240-6. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.01.037. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Vaccine. 2014. PMID: 24486361 Free PMC article.
-
Persistence of protection against hepatitis B virus infection among adolescents vaccinated with recombinant hepatitis B vaccine beginning at birth: a 15-year follow-up study.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2008 Oct;27(10):881-5. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31817702ba. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2008. PMID: 18756185
-
Immunogenicity of two paediatric doses of monovalent hepatitis B or combined hepatitis A and B vaccine in 8-10-year-old children.Vaccine. 2005 Jul 1;23(31):4082-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.07.022. Epub 2004 Aug 9. Vaccine. 2005. PMID: 15963363 Clinical Trial.
-
Booster dose vaccination for preventing hepatitis B.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jun 7;2016(6):CD008256. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008256.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27271960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccine induced immunologic memory for hepatitis B surface antigen: implications for policy on booster vaccination.Vaccine. 1996 Aug;14(11):1019-27. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(96)00062-x. Vaccine. 1996. PMID: 8879096 Review.
Cited by
-
Edible plants for oral delivery of biopharmaceuticals.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Jan;83(1):71-81. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12949. Epub 2016 May 9. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27037892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microneedle-Mediated Vaccine Delivery to the Oral Mucosa.Adv Healthc Mater. 2019 Feb;8(4):e1801180. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201801180. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019. PMID: 30537400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Micropropagation of transgenic lettuce containing HBsAg as a method of mass-scale production of standardised plant material for biofarming purposes.Plant Cell Rep. 2017 Jan;36(1):49-60. doi: 10.1007/s00299-016-2056-1. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Plant Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 27655251 Free PMC article.
-
The Last Ten Years of Advancements in Plant-Derived Recombinant Vaccines against Hepatitis B.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Oct 13;17(10):1715. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101715. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27754367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is There an Optimal Formulation and Delivery Strategy for Subunit Vaccines?Pharm Res. 2016 Sep;33(9):2078-97. doi: 10.1007/s11095-016-1979-0. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Pharm Res. 2016. PMID: 27380191 Review.
References
-
- CDC A comprehensive immunization strategy to eliminate transmission of hepatitis B virus infection in the united states. Pediatrics. 2006;118(1):404–404. - PubMed
-
- Ott JJ, et al. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: New estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity. Vaccine. 2012;30(12):2212–2219. - PubMed
-
- Hayden CA. An oral vaccine for hepatitis B: challenges, setbacks, and breakthroughs. In: Howard J.A.a.H., E. E., editors. Commercial plant-produced recombinant protein products: Case studies. Springer-Verlab; Heidelberg: 2014. pp. 197–228.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

