Comparative Biochemical and Functional Analysis of Viral and Human Secreted Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Decoy Receptors
- PMID: 25940088
- PMCID: PMC4481203
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.650119
Comparative Biochemical and Functional Analysis of Viral and Human Secreted Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Decoy Receptors
Abstract
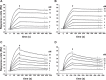
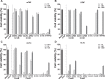
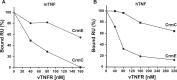
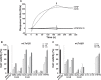
The blockade of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) by etanercept, a soluble version of the human TNF receptor 2 (hTNFR2), is a well established strategy to inhibit adverse TNF-mediated inflammatory responses in the clinic. A similar strategy is employed by poxviruses, encoding four viral TNF decoy receptor homologues (vTNFRs) named cytokine response modifier B (CrmB), CrmC, CrmD, and CrmE. These vTNFRs are differentially expressed by poxviral species, suggesting distinct immunomodulatory properties. Whereas the human variola virus and mouse ectromelia virus encode one vTNFR, the broad host range cowpox virus encodes all vTNFRs. We report the first comprehensive study of the functional and binding properties of these four vTNFRs, providing an explanation for their expression profile among different poxviruses. In addition, the vTNFRs activities were compared with the hTNFR2 used in the clinic. Interestingly, CrmB from variola virus, the causative agent of smallpox, is the most potent TNFR of those tested here including hTNFR2. Furthermore, we demonstrate a new immunomodulatory activity of vTNFRs, showing that CrmB and CrmD also inhibit the activity of lymphotoxin β. Similarly, we report for the first time that the hTNFR2 blocks the biological activity of lymphotoxin β. The characterization of vTNFRs optimized during virus-host evolution to modulate the host immune response provides relevant information about their potential role in pathogenesis and may be used to improve anti-inflammatory therapies based on soluble decoy TNFRs.
Keywords: TNF ligand superfamily; etanercept; immune evasion; inflammation; poxvirus; receptor; tumor necrosis factor (TNF); vTNFR; virus.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TNF Decoy Receptors Encoded by Poxviruses.Pathogens. 2021 Aug 22;10(8):1065. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10081065. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34451529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into ligand binding by a viral tumor necrosis factor (TNF) decoy receptor yield a selective soluble human type 2 TNF receptor.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 29;294(13):5214-5227. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005828. Epub 2019 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30723161 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinia virus strains Lister, USSR and Evans express soluble and cell-surface tumour necrosis factor receptors.J Gen Virol. 1999 Apr;80 ( Pt 4):949-959. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-80-4-949. J Gen Virol. 1999. PMID: 10211965
-
Properties of the recombinant TNF-binding proteins from variola, monkeypox, and cowpox viruses are different.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Nov;1764(11):1710-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2006.09.006. Epub 2006 Sep 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 17070121 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptors encoded by poxviruses.Mol Genet Metab. 1999 Aug;67(4):278-82. doi: 10.1006/mgme.1999.2878. Mol Genet Metab. 1999. PMID: 10444338 Review.
Cited by
-
Subversion of natural killer cell responses by a cytomegalovirus-encoded soluble CD48 decoy receptor.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Apr 4;15(4):e1007658. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007658. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30947296 Free PMC article.
-
TNF Decoy Receptors Encoded by Poxviruses.Pathogens. 2021 Aug 22;10(8):1065. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10081065. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34451529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokines cooperate with TNF to provide protective anti-viral immunity and to enhance inflammation.Nat Commun. 2018 May 3;9(1):1790. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04098-8. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29724993 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing poxviral know-how for anti-cytokine therapies.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 29;294(13):5228-5229. doi: 10.1074/jbc.H119.008151. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30926761 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into ligand binding by a viral tumor necrosis factor (TNF) decoy receptor yield a selective soluble human type 2 TNF receptor.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 29;294(13):5214-5227. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005828. Epub 2019 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30723161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggarwal B. B. (2003) Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 745–756 - PubMed
-
- Black R. A., Rauch C. T., Kozlosky C. J., Peschon J. J., Slack J. L., Wolfson M. F., Castner B. J., Stocking K. L., Reddy P., Srinivasan S., Nelson N., Boiani N., Schooley K. A., Gerhart M., Davis R., Fitzner J. N., Johnson R. S., Paxton R. J., March C. J., Cerretti D. P. (1997) A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumour necrosis factor-α from cells. Nature 385, 729–733 - PubMed
-
- Browning J. L., Ngam-ek A., Lawton P., DeMarinis J., Tizard R., Chow E. P., Hession C., O'Brine-Greco B., Foley S. F., Ware C. F. (1993) Lymphotoxin β, a novel member of the TNF family that forms a heteromeric complex with lymphotoxin on the cell surface. Cell 72, 847–856 - PubMed
-
- Crowe P. D., VanArsdale T. L., Walter B. N., Ware C. F., Hession C., Ehrenfels B., Browning J. L., Din W. S., Goodwin R. G., Smith C. A. (1994) A lymphotoxin-β-specific receptor. Science 264, 707–710 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

