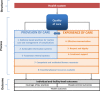
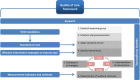
Quality of care for pregnant women and newborns-the WHO vision
- PMID: 25929823
- PMCID: PMC5029576
- DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.13451
Quality of care for pregnant women and newborns-the WHO vision
Figures
Comment in
-
Re: Quality of care for pregnant women and newborns-the WHO vision: WHO vision for Quality of Care for pregnant women and newborns: a welcome initiative.BJOG. 2016 Jan;123(1):144-5. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.13747. BJOG. 2016. PMID: 26715347 No abstract available.
-
Authors' reply re: Quality of care for pregnant women and newborns-the WHO vision.BJOG. 2016 Jan;123(1):145. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.13748. BJOG. 2016. PMID: 26715349 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Re: Quality of care for pregnant women and newborns-the WHO vision: WHO vision for Quality of Care for pregnant women and newborns: a welcome initiative.BJOG. 2016 Jan;123(1):144-5. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.13747. BJOG. 2016. PMID: 26715347 No abstract available.
-
Authors' reply re: Quality of care for pregnant women and newborns-the WHO vision.BJOG. 2016 Jan;123(1):145. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.13748. BJOG. 2016. PMID: 26715349 No abstract available.
-
[Further improvement of medical care of pregnant women and and newborns in the RSFSR].Vopr Okhr Materin Det. 1975 Sep;20(9):3-8. Vopr Okhr Materin Det. 1975. PMID: 1224544 Russian. No abstract available.
-
Joint position paper on rural maternity care.Can J Rural Med. 2012 Fall;17(4):135-41, E1-9. Can J Rural Med. 2012. PMID: 23017345 Review. English, French. No abstract available.
-
Public health nursing evaluation, education, and professional issues: 1977 to 1981.Annu Rev Nurs Res. 1984;2:165-89. Annu Rev Nurs Res. 1984. PMID: 6388600 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
"I fought my entire way": Experiences of declining maternity care services in British Columbia.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 4;16(6):e0252645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252645. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34086795 Free PMC article.
-
Women's experiences and needs concerning care and support during the various phases of childbirth and the postnatal period: Analysis of free-text comments based on Quality from the Patient's Perspective in Sweden.Eur J Midwifery. 2024 Feb 19;8. doi: 10.18332/ejm/176698. eCollection 2024. Eur J Midwifery. 2024. PMID: 38375418 Free PMC article.
-
What Prevents Quality Midwifery Care? A Systematic Mapping of Barriers in Low and Middle Income Countries from the Provider Perspective.PLoS One. 2016 May 2;11(5):e0153391. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153391. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27135248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experiences of breastfeeding peer counseling among women with low incomes in the US: a qualitative evaluation.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Feb 9;24(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-06213-0. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 38336607 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Health Insurance and access to maternal healthcare services among Peruvian women: a cross-sectional study using the 2021 national demographic survey.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 Nov 15;23(1):795. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-06086-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023. PMID: 37968607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United Nations Secretary‐General . Global Strategy for Women's and Children's Health. New York: UN, 2010.
-
- Campbell OM, Graham WJ. Lancet Maternal Survival Series steering group. Strategies for reducing maternal mortality: getting on with what works. Lancet 2006;368:1284–99. - PubMed
-
- Global Health Group . Where Women go to Deliver: Overview of the Project and Review of Preliminary Findings. San Francisco: UCSF Global Health Sciences, 2014.
-
- United Nations . The Millennium Development Goals Report 2014. New York: UN, 2014.
-
- Souza JP, Gulmezoglu AM, Vogel J, Carroli G, Lumbiganon P, Qureshi Z, et al. Moving beyond essential interventions for reduction of maternal mortality (the WHO Multicountry Survey on Maternal and Newborn Health): a cross‐sectional study. Lancet 2013;381:1747–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical