TSLP is differentially regulated by vitamin D3 and cytokines in human skin
- PMID: 25866638
- PMCID: PMC4386913
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.48
TSLP is differentially regulated by vitamin D3 and cytokines in human skin
Abstract
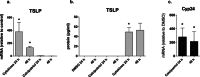
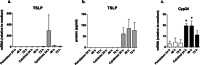
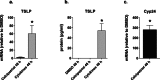
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) plays an important role in allergic diseases and is highly expressed in keratinocytes in human lesional atopic dermatitis (AD) skin. In nonlesional AD skin TSLP expression can be induced by applying house dust mite allergen onto the skin in the atopy patch test. Several studies have demonstrated that the induction of TSLP expression in mouse skin does not only lead to AD-like inflammation of the skin, but also predisposes to severe inflammation of the airways. In mice, TSLP expression can be induced by application of the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (VD3) analogue calcipotriol and results in the development of eczema-like lesions. The objective is to investigate the effect of VD3 (calcitriol) or calcipotriol on TSLP expression in normal human skin and skin from AD patients. Using multiple ex vivo experimental setups, the effects of calci(po)triol on TSLP expression by normal human skin, and skin from AD patients were investigated and compared to effects of calcipotriol on mouse and non-human primates (NHP) skin. No induction of TSLP expression (mRNA or protein) was observed in human keratinocytes, normal human skin, nonlesional AD skin, or NHP skin samples after stimulation with calcipotriol or topical application of calcitriol. The biological activity of calci(po)triol in human skin samples was demonstrated by the increased expression of the VD3-responsive Cyp24a1 gene. TSLP expression was induced by cytokines (IL-4, IL-13, and TNF-α) in skin samples from all three species. In contrast to the findings in human and NHP, a consistent increase in TSLP expression was confirmed in mouse skin biopsies after stimulation with calcipotriol. VD3 failed to induce expression of TSLP in human or monkey skin in contrast to mouse, implicating careful extrapolation of this often-used mouse model to AD patients.
Keywords: Allergy; TSLP; VDRE; atopic dermatitis; vitamin D3.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dexamethasone but not tacrolimus suppresses TNF-α-induced thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression in lesional keratinocytes of atopic dermatitis model.J Dermatol Sci. 2015 Oct;80(1):45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2015.06.016. Epub 2015 Jul 3. J Dermatol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26198442
-
Topical vitamin D3 and low-calcemic analogs induce thymic stromal lymphopoietin in mouse keratinocytes and trigger an atopic dermatitis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 1;103(31):11736-41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604575103. Epub 2006 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16880407 Free PMC article.
-
Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid aggravates calcipotriol-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in mice by increasing the expression of thymic stromal lymphopoietin.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Feb;10(4):209. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-282. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35280398 Free PMC article.
-
Oral vitamin D modulates the epidermal expression of the vitamin D receptor and cathelicidin in children with atopic dermatitis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2023 May;315(4):761-770. doi: 10.1007/s00403-022-02416-1. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023. PMID: 36273083
-
Expression of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in canine atopic dermatitis.Vet Dermatol. 2013 Feb;24(1):54-9.e13-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3164.2012.01096.x. Vet Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 23331680
Cited by
-
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin induces adipose loss through sebum hypersecretion.Science. 2021 Jul 30;373(6554):eabd2893. doi: 10.1126/science.abd2893. Science. 2021. PMID: 34326208 Free PMC article.
-
Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Cancer: Th2-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 16;11:2088. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02088. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33042121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin: To Cut a Long Story Short.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Jan 17;3(2):174-182. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2017.01.005. eCollection 2017 Mar. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28275684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of topical anthralin and calcipotriene in alopecia areata: A discussion of the mechanisms of action.JAAD Case Rep. 2020 May 22;6(7):673-674. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.05.022. eCollection 2020 Jul. JAAD Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32743037 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The role of basophils as innate immune regulatory cells in allergy and immunotherapy.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2018 Apr 3;14(4):815-831. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2017.1417711. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2018. PMID: 29257936 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ramasamy A, Curjuric I, Coin LJ, Kumar A, McArdle, WL, Imboden M, et al. A genome-wide meta-analysis of genetic variants associated with allergic rhinitis and grass sensitization and their interaction with birth order. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011;128(5):996–1005. - PubMed
-
- Soumelis V, Reche PA, Kanzler H, Yuan W, Edward, G, Homey B, et al. Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat. Immunol. 2002;3(7):673–680. - PubMed
-
- Landheer J, Giovannone B, Mattson JD, Tjabringa S, Bruijnzeel-Koomen, CA, McClanahan T, et al. Epicutaneous application of house dust mite induces thymic stromal lymphopoietin in nonlesional skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013;132(5):1252–1254. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

