Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and 2 predict outcomes in advanced chronic kidney disease: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 25823004
- PMCID: PMC4379033
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122073
Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and 2 predict outcomes in advanced chronic kidney disease: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors 1 (sTNFR1) and 2 (sTNFR2) have been associated to progression of renal failure, end stage renal disease and mortality in early stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD), mostly in the context of diabetic nephropathy. The predictive value of these markers in advanced stages of CKD irrespective of the specific causes of kidney disease has not yet been defined. In this study, the relationship between sTNFR1 and sTNFR2 and the risk for adverse cardiovascular events (CVE) and all-cause mortality was investigated in a population with CKD stage 4-5, not yet on dialysis, to minimize the confounding by renal function.
Patients and methods: In 131 patients, CKD stage 4-5, sTNFR1, sTNFR2 were analysed for their association to a composite endpoint of all-cause mortality or first non-fatal CVE by univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards models. In the multivariate models, age, gender, CRP, eGFR and significant comorbidities were included as covariates.
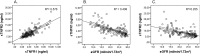
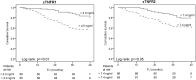
Results: During a median follow-up of 33 months, 40 events (30.5%) occurred of which 29 deaths (22.1%) and 11 (8.4%) first non-fatal CVE. In univariate analysis, the hazard ratios (HR) of sTNFR1 and sTNFR2 for negative outcome were 1.49 (95% confidence interval (CI): 1.28-1.75) and 1.13 (95% CI: 1.06-1.20) respectively. After adjustment for clinical covariables (age, CRP, diabetes and a history of cardiovascular disease) both sTNFRs remained independently associated to outcomes (HR: sTNFR1: 1.51, 95% CI: 1.30-1.77; sTNFR2: 1.13, 95% CI: 1.06-1.20). A subanalysis of the non-diabetic patients in the study population confirmed these findings, especially for sTNFR1.
Conclusion: sTNFR1 and sTNFR2 are independently associated to all-cause mortality or an increased risk for cardiovascular events in advanced CKD irrespective of the cause of kidney disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors 1 and 2 with nephropathy, cardiovascular events, and total mortality in type 2 diabetes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016 Feb 29;15:40. doi: 10.1186/s12933-016-0359-8. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016. PMID: 26928194 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (sTNFR1) is associated with increased total mortality due to cancer and cardiovascular causes - findings from two community based cohorts of elderly.Atherosclerosis. 2014 Nov;237(1):236-42. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.09.005. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Atherosclerosis. 2014. PMID: 25255422
-
Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 is associated with diminished estimated glomerular filtration rate in colombian patients with type 2 diabetes.J Diabetes Complications. 2016 Jul;30(5):852-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.03.015. Epub 2016 Mar 17. J Diabetes Complications. 2016. PMID: 27068267
-
The Signaling Pathway of TNF Receptors: Linking Animal Models of Renal Disease to Human CKD.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 18;23(6):3284. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063284. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabonomic biomarkers for risk factors of chronic kidney disease.Int Urol Nephrol. 2016 Apr;48(4):547-52. doi: 10.1007/s11255-016-1239-6. Epub 2016 Feb 20. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26897037 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel therapeutic vaccine targeting the soluble TNFα receptor II to limit the progression of cardiovascular disease: AtheroVax™.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jul 18;10:1206541. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1206541. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37534280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum tenascin-C is independently associated with increased major adverse cardiovascular events and death in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a French prospective cohort.Diabetologia. 2020 May;63(5):915-923. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05108-5. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Diabetologia. 2020. PMID: 32040670
-
Murine Nephrotoxic Nephritis as a Model of Chronic Kidney Disease.Int J Nephrol. 2018 Mar 5;2018:8424502. doi: 10.1155/2018/8424502. eCollection 2018. Int J Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29692933 Free PMC article.
-
Host factors associated with serologic inflammatory markers assessed using multiplex assays.Cytokine. 2016 Sep;85:71-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.05.016. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Cytokine. 2016. PMID: 27295613 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenome-Wide Association Study of Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 2 Levels in the Framingham Heart Study.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Apr 24;9:207. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00207. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29740313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weiner DE, Tighiouart H, Amin MG, Stark PC, MacLeod B, Griffith JL, et al. Chronic Kidney Disease as a Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality: A Pooled Analysis of Community-Based Studies. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004; 15: 1307–15. - PubMed
-
- Shlipak MG, Fried LF, Cushman M, Manolio TA, Peterson D, Stehman-Breen C, et al. Cardiovascular mortality risk in chronic kidney disease—Comparison of traditional and novel risk factors. Jama-Journal of the American Medical Association. 2005; 293: 1737–45. - PubMed
-
- Soriano S, Gonzalez L, Martin-Malo A, Rodriguez M, Aljama P. C-reactive protein and low albumin are predictors of morbidity and cardiovascular events in chronic kidney disease (CKD) 3–5 patients. Clin Nephrol. 2007; 67: 352–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

