Gammaherpesvirus small noncoding RNAs are bifunctional elements that regulate infection and contribute to virulence in vivo
- PMID: 25691585
- PMCID: PMC4337559
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.01670-14
Gammaherpesvirus small noncoding RNAs are bifunctional elements that regulate infection and contribute to virulence in vivo
Abstract
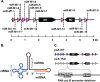
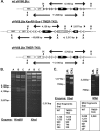
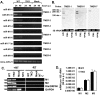
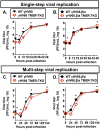
Many viruses express noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs). The gammaherpesviruses (γHVs), including Epstein-Barr virus, Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, and murine γHV68, each contain multiple ncRNA genes, including microRNAs (miRNAs). While these ncRNAs can regulate multiple host and viral processes in vitro, the genetic contribution of these RNAs to infection and pathogenesis remains largely unknown. To study the functional contribution of these RNAs to γHV infection, we have used γHV68, a small-animal model of γHV pathogenesis. γHV68 encodes eight small hybrid ncRNAs that contain both tRNA-like elements and functional miRNAs. These genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase III and are referred to as the γHV68 TMERs (tRNA-miRNA-encoded RNAs). To determine the total concerted genetic contribution of these ncRNAs to γHV acute infection and pathogenesis, we generated and characterized a recombinant γHV68 strain devoid of all eight TMERs. TMER-deficient γHV68 has wild-type levels of lytic replication in vitro and normal establishment of latency in B cells early following acute infection in vivo. In contrast, during acute infection of immunodeficient mice, TMER-deficient γHV68 has reduced virulence in a model of viral pneumonia, despite having an enhanced frequency of virus-infected cells. Strikingly, expression of a single viral tRNA-like molecule, in the absence of all other virus-encoded TMERs and miRNAs, reverses both attenuation in virulence and enhanced frequency of infected cells. These data show that γHV ncRNAs play critical roles in acute infection and virulence in immunocompromised hosts and identify these RNAs as a new potential target to modulate γHV-induced infection and pathogenesis.
Importance: The gammaherpesviruses (γHVs) are a subfamily of viruses associated with chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. These viruses uniformly encode multiple types of noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) that are not translated into proteins. It remains unclear how virus-expressed ncRNAs influence the course and outcome of infection in vivo. Here, we generated a mouse γHV that lacks the expression of multiple ncRNAs. Notably, this mutant virus is critically impaired in the ability to cause disease in immunocompromised hosts yet shows a paradoxical increase in infected cells early during infection in these hosts. While the original mouse virus encodes multiple ncRNAs, the expression of a single domain of one ncRNA can partially reverse the defects of the mutant virus. These studies demonstrate that γHV ncRNAs can directly contribute to virus-induced disease in vivo and that these RNAs may be multifunctional, allowing the opportunity to specifically interfere with different functional domains of these RNAs.
Copyright © 2015 Diebel et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Gammaherpesvirus Noncoding RNA Is Essential for Hematogenous Dissemination and Establishment of Peripheral Latency.mSphere. 2016 Apr;1(2):e00105-15. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00105-15. Epub 2016 Mar 2. mSphere. 2016. PMID: 27110595 Free PMC article.
-
Lytic Infection with Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68 Activates Host and Viral RNA Polymerase III Promoters and Enhances Noncoding RNA Expression.J Virol. 2021 Jun 24;95(14):e0007921. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00079-21. Epub 2021 Jun 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33910955 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-encoded microRNAs facilitate gammaherpesvirus latency and pathogenesis in vivo.mBio. 2014 May 27;5(3):e00981-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00981-14. mBio. 2014. PMID: 24865551 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of non-coding RNAs in viral infections.Rev Med Virol. 2016 Sep;26(5):356-68. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1893. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Rev Med Virol. 2016. PMID: 27401792 Review.
-
EBV Noncoding RNAs.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:181-217. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_6. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428375 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-3470b promotes bovine ephemeral fever virus replication via directly targeting mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS) in baby hamster Syrian kidney cells.BMC Microbiol. 2018 Dec 27;18(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1366-6. BMC Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30587113 Free PMC article.
-
The gammaherpesvirus 68 viral cyclin facilitates expression of LANA.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Nov 15;17(11):e1010019. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010019. eCollection 2021 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34780571 Free PMC article.
-
Host Tumor Suppressor p18INK4c Functions as a Potent Cell-Intrinsic Inhibitor of Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68 Reactivation and Pathogenesis.J Virol. 2018 Feb 26;92(6):e01604-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01604-17. Print 2018 Mar 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29298882 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Non-coding RNAs During Herpesvirus Infection.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2018;419:243-280. doi: 10.1007/82_2017_31. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28674945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Ribosomal RNA-Derived Resident MicroRNAs as the Transmitter of Information upon the Cytoplasmic Cancer Stress.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:7562085. doi: 10.1155/2016/7562085. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27517048 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

