Rice stripe virus affects the viability of its vector offspring by changing developmental gene expression in embryos
- PMID: 25601039
- PMCID: PMC4298728
- DOI: 10.1038/srep07883
Rice stripe virus affects the viability of its vector offspring by changing developmental gene expression in embryos
Abstract
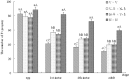
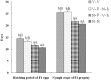
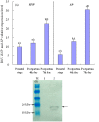
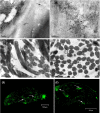
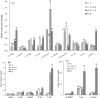
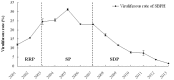
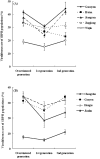
Plant viruses may affect the viability and development process of their herbivore vectors. Small brown planthopper (SBPH) is main vector of Rice stripe virus (RSV), which causes serious rice stripe disease. Here, we reported the effects of RSV on SBPH offspring by crossing experiments between viruliferous and non-viruliferous strains. The life parameters of offspring from different cross combinations were compared. The hatchability of F1 progeny from viruliferous parents decreased significantly, and viruliferous rate was completely controlled by viruliferous maternal parent. To better elucidate the underlying biological mechanisms, the morphology of eggs, viral propagation and distribution in the eggs and expression profile of embryonic development genes were investigated. The results indicated that RSV replicated and accumulated in SBPH eggs resulting in developmental stunt or delay of partial eggs; in addition, RSV was only able to infect ovum but not sperm. According to the expression profile, expression of 13 developmental genes was regulated in the eggs from viruliferous parents, in which two important regulatory genes (Ls-Dorsal and Ls-CPO) were most significantly down-regulated. In general, RSV exerts an adverse effect on SBPH, which is unfavourable for the expansion of viruliferous populations. The viewpoint is also supported by systematic monitoring of SBPH viruliferous rate.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Viruliferous rate of small brown planthopper is a good indicator of rice stripe disease epidemics.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 22;6:21376. doi: 10.1038/srep21376. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26898155 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Chemoreception Organs of Laodelphax striatellus in Response to Rice Stripe Virus Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 24;22(19):10299. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910299. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638638 Free PMC article.
-
Rice stripe virus-derived siRNAs play different regulatory roles in rice and in the insect vector Laodelphax striatellus.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Oct 4;18(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1438-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30286719 Free PMC article.
-
The small brown planthopper (Laodelphax striatellus) as a vector of the rice stripe virus.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2023 Feb;112(2):e21992. doi: 10.1002/arch.21992. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36575628 Review.
-
Rice Responses and Resistance to Planthopper-Borne Viruses at Transcriptomic and Proteomic Levels.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2016;19:43-52. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26363817 Review.
Cited by
-
Rice stripe virus counters reduced fecundity in its insect vector by modifying insect physiology, primary endosymbionts and feeding behavior.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 27;5:12527. doi: 10.1038/srep12527. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26211618 Free PMC article.
-
The Bunyavirales: The Plant-Infecting Counterparts.Viruses. 2021 May 6;13(5):842. doi: 10.3390/v13050842. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34066457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viruliferous rate of small brown planthopper is a good indicator of rice stripe disease epidemics.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 22;6:21376. doi: 10.1038/srep21376. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26898155 Free PMC article.
-
Rice Stripe Virus Infection Alters mRNA Levels of Sphingolipid-Metabolizing Enzymes and Sphingolipids Content in Laodelphax striatellus.J Insect Sci. 2017 Jan 27;17(1):16. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/iew111. Print 2017 Jan. J Insect Sci. 2017. PMID: 28130458 Free PMC article.
-
Rice Stripe Virus Coat Protein-Mediated Virus Resistance Is Associated With RNA Silencing in Arabidopsis.Front Microbiol. 2020 Nov 13;11:591619. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.591619. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33281789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou Y. J., Li S., Cheng Z. B., Zhou T. & Fan Y. J. Research advances in rice stripe disease in China. Jiangsu J. of Agr. Sci. 28, 1007–1015 (2012).
-
- Falk B. W. & Tsai J. H. Biology and molecular biology of viruses in the genus Tenuivirus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 36, 139–163 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Suzuki Y., Fuji S., Takahashi Y. & Kojima M. Immunogold localization of rice stripe virus particle antigen in thin sections of insect host cells. Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Jpn. 58, 480–484 (1992).
-
- Liang D., Qu Z., Ma X. & Hull R. Detection and localization of Rice stripe virus gene products in vivo. Virus Genes 31, 211–221 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

