Identification of RNA polymerase III-transcribed Alu loci by computational screening of RNA-Seq data
- PMID: 25550429
- PMCID: PMC4333407
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku1361
Identification of RNA polymerase III-transcribed Alu loci by computational screening of RNA-Seq data
Abstract
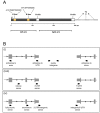
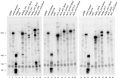
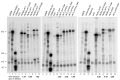
Of the ∼ 1.3 million Alu elements in the human genome, only a tiny number are estimated to be active in transcription by RNA polymerase (Pol) III. Tracing the individual loci from which Alu transcripts originate is complicated by their highly repetitive nature. By exploiting RNA-Seq data sets and unique Alu DNA sequences, we devised a bioinformatic pipeline allowing us to identify Pol III-dependent transcripts of individual Alu elements. When applied to ENCODE transcriptomes of seven human cell lines, this search strategy identified ∼ 1300 Alu loci corresponding to detectable transcripts, with ∼ 120 of them expressed in at least three cell lines. In vitro transcription of selected Alus did not reflect their in vivo expression properties, and required the native 5'-flanking region in addition to internal promoter. We also identified a cluster of expressed AluYa5-derived transcription units, juxtaposed to snaR genes on chromosome 19, formed by a promoter-containing left monomer fused to an Alu-unrelated downstream moiety. Autonomous Pol III transcription was also revealed for Alus nested within Pol II-transcribed genes. The ability to investigate Alu transcriptomes at single-locus resolution will facilitate both the identification of novel biologically relevant Alu RNAs and the assessment of Alu expression alteration under pathological conditions.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evolution and distribution of RNA polymerase II regulatory sites from RNA polymerase III dependant mobile Alu elements.BMC Evol Biol. 2004 Oct 4;4:37. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-4-37. BMC Evol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15461819 Free PMC article.
-
Specific binding sites for a pol III transcriptional repressor and pol II transcription factor YY1 within the internucleosomal spacer region in primate Alu repetitive elements.Gene Expr. 1996;6(3):151-68. Gene Expr. 1996. PMID: 9041122 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of polymerase III-transcribed Alu elements suggests cell-type-specific enhancer function.Genome Res. 2019 Sep;29(9):1402-1414. doi: 10.1101/gr.249789.119. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Genome Res. 2019. PMID: 31413151 Free PMC article.
-
ALUternative Regulation for Gene Expression.Trends Cell Biol. 2017 Jul;27(7):480-490. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Trends Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28209295 Review.
-
From 'JUNK' to just unexplored noncoding knowledge: the case of transcribed Alus.Brief Funct Genomics. 2011 Sep;10(5):294-311. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elr029. Brief Funct Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21987713 Review.
Cited by
-
Perlman syndrome nuclease DIS3L2 controls cytoplasmic non-coding RNAs and provides surveillance pathway for maturing snRNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Dec 1;44(21):10437-10453. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw649. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27431325 Free PMC article.
-
TATA-Like Boxes in RNA Polymerase III Promoters: Requirements for Nucleotide Sequences.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 25;21(10):3706. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103706. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32466110 Free PMC article.
-
Alu-miRNA interactions modulate transcript isoform diversity in stress response and reveal signatures of positive selection.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 2;6:32348. doi: 10.1038/srep32348. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27586304 Free PMC article.
-
RNA transcription and degradation of Alu retrotransposons depends on sequence features and evolutionary history.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 May 6;12(5):jkac054. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac054. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35253846 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus small E1A directs activation of Alu transcription at YAP/TEAD- and AP-1-bound enhancers through interactions with the EP400 chromatin remodeler.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Sep 9;52(16):9481-9500. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae615. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39011896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dieci G., Conti A., Pagano A., Carnevali D. Identification of RNA polymerase III-transcribed genes in eukaryotic genomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013;1829:296–305. - PubMed
-
- Orioli A., Pascali C., Pagano A., Teichmann M., Dieci G. RNA polymerase III transcription control elements: themes and variations. Gene. 2012;493:185–194. - PubMed

