The role of AMPA receptors in postsynaptic mechanisms of synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 25505875
- PMCID: PMC4245900
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00401
The role of AMPA receptors in postsynaptic mechanisms of synaptic plasticity
Abstract
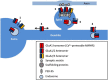
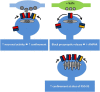
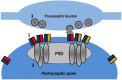
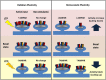
In the mammalian central nervous system, excitatory glutamatergic synapses harness neurotransmission that is mediated by ion flow through α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors (AMPARs). AMPARs, which are enriched in the postsynaptic membrane on dendritic spines, are highly dynamic, and shuttle in and out of synapses in an activity-dependent manner. Changes in their number, subunit composition, phosphorylation state, and accessory proteins can all regulate AMPARs and thus modify synaptic strength and support cellular forms of learning. Furthermore, dysregulation of AMPAR plasticity has been implicated in various pathological states and has important consequences for mental health. Here we focus on the mechanisms that control AMPAR plasticity, drawing particularly from the extensive studies on hippocampal synapses, and highlight recent advances in the field along with considerations for future directions.
Keywords: AMPAR; Hebbian plasticity; homeostatic plasticity; synaptic plasticity; synaptic transmission; trafficking.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Control of Homeostatic Synaptic Plasticity by AKAP-Anchored Kinase and Phosphatase Regulation of Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptors.J Neurosci. 2018 Mar 14;38(11):2863-2876. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2362-17.2018. Epub 2018 Feb 13. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29440558 Free PMC article.
-
AMPAR trafficking in synapse maturation and plasticity.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Dec;70(23):4411-30. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1309-1. Epub 2013 Mar 9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23475111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation-Dependent Regulation of Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptors During Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2020 Mar 27;12:8. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2020.00008. eCollection 2020. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32292336 Free PMC article.
-
The deubiquitinating enzyme USP46 regulates AMPA receptor ubiquitination and trafficking.J Neurochem. 2015 Sep;134(6):1067-80. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13194. Epub 2015 Jul 16. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26077708 Free PMC article.
-
The Shaping of AMPA Receptor Surface Distribution by Neuronal Activity.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022 Mar 21;14:833782. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2022.833782. eCollection 2022. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35387308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sex differences in glutamate transmission and plasticity in reward related regions.Front Behav Neurosci. 2024 Sep 18;18:1455478. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2024.1455478. eCollection 2024. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39359325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxytocin signaling is necessary for synaptic maturation of adult-born neurons.Genes Dev. 2022 Nov-Dec 1;36(21-24):1100-1118. doi: 10.1101/gad.349930.122. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Genes Dev. 2022. PMID: 36617877 Free PMC article.
-
Postsynaptic Syntaxin 4 negatively regulates the efficiency of neurotransmitter release.J Neurogenet. 2018 Sep;32(3):221-229. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2018.1501372. Epub 2018 Sep 3. J Neurogenet. 2018. PMID: 30175640 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-dependent and NMDA receptor-dependent LTP and LTD share the common AMPAR trafficking pathway.iScience. 2023 Feb 3;26(3):106133. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106133. eCollection 2023 Mar 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 36866246 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulation of AMPA Receptor Endocytosis by Dynamic Protein-Protein Interactions.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Oct 11;12:362. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00362. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30364226 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

