Tadalafil reduces myeloid-derived suppressor cells and regulatory T cells and promotes tumor immunity in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 25320361
- PMCID: PMC4322895
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1711
Tadalafil reduces myeloid-derived suppressor cells and regulatory T cells and promotes tumor immunity in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) and regulatory T cells (Treg) play a key role in the progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). On the basis of our preclinical data demonstrating that phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibition can modulate these cell populations, we evaluated whether the PDE5 inhibitor tadalafil can revert tumor-induced immunosuppression and promote tumor immunity in patients with HNSCC.
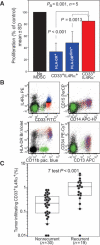
Experimental design: First, we functionally and phenotypically characterized MDSCs in HNSCCs and determined, retrospectively, whether their presence at the tumor site correlates with recurrence. Then, we performed a prospective single-center, double-blinded, randomized, three-arm study in which patients with HNSCC undergoing definitive surgical resection of oral and oropharyngeal tumors were treated with tadalafil 10 mg/day, 20 mg/day, or placebo for at least 20 days preoperatively. Blood and tumor MDSC and Treg presence and CD8(+) T-cell reactivity to tumor antigens were evaluated before and after treatment.
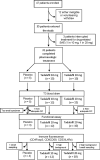
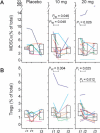
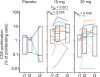
Results: MDSCs were characterized in HNSCC and their intratumoral presence significantly correlates with recurrence. Tadalafil treatment was well tolerated and significantly reduced both MDSCs and Treg concentrations in the blood and in the tumor (P < 0.05). In addition, the concentration of blood CD8(+) T cells reactive to autologous tumor antigens significantly increased after treatment (P < 0.05). Tadalafil immunomodulatory activity was maximized at an intermediate dose but not at higher doses. Mechanistic analysis suggests a possible off-target effect on PDE11 at high dosages that, by increasing intracellular cAMP, may negatively affect antitumor immunity.
Conclusions: Tadalafil seems to beneficially modulate the tumor micro- and macro-environment in patients with HNSCC by lowering MDSCs and Tregs and increasing tumor-specific CD8(+) T cells in a dose-dependent fashion.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tadalafil augments tumor specific immunity in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Jan 1;21(1):30-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1716. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25564570 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
γ-Secretase inhibitor reduces immunosuppressive cells and enhances tumour immunity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2018 Mar 1;142(5):999-1009. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31115. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29047105
-
The Reversal of Immune Exclusion Mediated by Tadalafil and an Anti-tumor Vaccine Also Induces PDL1 Upregulation in Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Interim Analysis of a Phase I Clinical Trial.Front Immunol. 2019 May 31;10:1206. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01206. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31214178 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2023;375:33-92. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2022.11.002. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36967154 Review.
-
Afatinib in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016 Jun;17(9):1295-301. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2016.1183647. Epub 2016 May 19. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27160335 Review.
Cited by
-
New Approaches in Oncology for Repositioning Drugs: The Case of PDE5 Inhibitor Sildenafil.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 26;11:627229. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.627229. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33718200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Escape Mechanisms and Their Clinical Relevance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 24;21(19):7032. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197032. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32987799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tadalafil Enhances Immune Signatures in Response to Neoadjuvant Nivolumab in Resectable Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 1;28(5):915-927. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1816. Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 34911681 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Immunotherapy of cancer: targeting cancer during active disease or during dormancy?Immunotherapy. 2017 Sep;9(11):943-949. doi: 10.2217/imt-2017-0044. Immunotherapy. 2017. PMID: 29338608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T-cell immunoglobulin mucin 3 blockade drives an antitumor immune response in head and neck cancer.Mol Oncol. 2017 Feb;11(2):235-247. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12029. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Mol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28102051 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howell GM, Grandis JR. Molecular mediators of metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2005;27:710–7. - PubMed
-
- Freiser ME, Serafini P, Weed DT. The immune system and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: from carcinogenesis to new therapeutic opportunities. Immunol Res. 2013;57:52–69. - PubMed
-
- Young MR, Wright MA, Lozano Y, Prechel MM, Benefield J, Leonetti JP, et al. Increased recurrence and metastasis in patients whose primary head and neck squamous cell carcinomas secreted granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and contained CD34+ natural suppressor cells. Int J Cancer. 1997;74:69–74. - PubMed
-
- Pak AS, Wright MA, Matthews JP, Collins SL, Petruzzelli GJ, Young MRI. Mechanisms of immune suppression in patients with head and neck cancer: presence of CD34(+) cells which suppress immune functions within cancers that secrete granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Clin Cancer Res. 1995;1:95–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

