Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded replication and transcription activator impairs innate immunity via ubiquitin-mediated degradation of myeloid differentiation factor 88
- PMID: 25320320
- PMCID: PMC4301122
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02591-14
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded replication and transcription activator impairs innate immunity via ubiquitin-mediated degradation of myeloid differentiation factor 88
Abstract
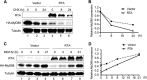
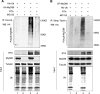
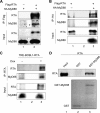
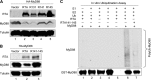
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is a human gammaherpesvirus with latent and lytic reactivation cycles. The mechanism by which KSHV evades the innate immune system to establish latency has not yet been precisely elucidated. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are the first line of defense against viral infections. Myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) is a key adaptor that interacts with all TLRs except TLR3 to produce inflammatory factors and type I interferons (IFNs), which are central components of innate immunity against microbial infection. Here, we found that KSHV replication and transcription activator (RTA), which is an immediate-early master switch protein of viral cycles, downregulates MyD88 expression at the protein level by degrading MyD88 through the ubiquitin (Ub)-proteasome pathway. We identified the interaction between RTA and MyD88 in vitro and in vivo and demonstrated that RTA functions as an E3 ligase to ubiquitinate MyD88. MyD88 also was repressed at the early stage of de novo infection as well as in lytic reactivation. We also found that RTA inhibited lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-triggered activation of the TLR4 pathway by reducing IFN production and NF-κB activity. Finally, we showed that MyD88 promoted the production of IFNs and inhibited KSHV LANA-1 gene transcription. Taken together, our results suggest that KSHV RTA facilitates the virus to evade innate immunity through the degradation of MyD88, which might be critical for viral latency control.
Importance: MyD88 is an adaptor for all TLRs other than TLR3, and it mediates inflammatory factors and IFN production. Our study demonstrated that the KSHV RTA protein functions as an E3 ligase to degrade MyD88 through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and block the transmission of TLRs signals. Moreover, we found that KSHV inhibited MyD88 expression during the early stage of de novo infection as well as in lytic reactivation. These results provide a potential mechanism for the virus to evade innate immunity.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Reduces Cellular Myeloid Differentiation Primary-Response Gene 88 (MyD88) Expression via Modulation of Its RNA.J Virol. 2015 Oct 14;90(1):180-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02342-15. Print 2016 Jan 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26468534 Free PMC article.
-
Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II HLA-DRα Is Downregulated by Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Encoded Lytic Transactivator RTA and MARCH8.J Virol. 2016 Aug 26;90(18):8047-58. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01079-16. Print 2016 Sep 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27356905 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus degrades cellular Toll-interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor-inducing beta-interferon (TRIF).J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 11;286(10):7865-7872. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.191452. Epub 2011 Jan 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21212282 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Degradation by Gammaherpesvirus RTAs: More Than Just Viral Transactivators.Viruses. 2023 Mar 11;15(3):730. doi: 10.3390/v15030730. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reactivation and Lytic Replication of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus: An Update.Front Microbiol. 2017 Apr 20;8:613. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00613. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28473805 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-step regulation of innate immune signaling by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.Virus Res. 2015 Nov 2;209:39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Virus Res. 2015. PMID: 25796211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
THO Complex Subunit 7 Homolog Negatively Regulates Cellular Antiviral Response against RNA Viruses by Targeting TBK1.Viruses. 2019 Feb 15;11(2):158. doi: 10.3390/v11020158. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30769920 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus and Innate Immunity: Friends or Foes?Microorganisms. 2019 Jun 24;7(6):183. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7060183. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31238570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Interplay between KSHV Infection and DNA-Sensing Pathways.Viruses. 2024 May 8;16(5):749. doi: 10.3390/v16050749. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38793630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening of the Human Kinome Identifies MSK1/2-CREB1 as an Essential Pathway Mediating Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Replication during Primary Infection.J Virol. 2015 Sep;89(18):9262-80. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01098-15. Epub 2015 Jun 24. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26109721 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

