miR-17-92 cluster promotes cholangiocarcinoma growth: evidence for PTEN as downstream target and IL-6/Stat3 as upstream activator
- PMID: 25239565
- PMCID: PMC4188863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.06.024
miR-17-92 cluster promotes cholangiocarcinoma growth: evidence for PTEN as downstream target and IL-6/Stat3 as upstream activator
Abstract
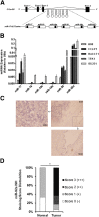
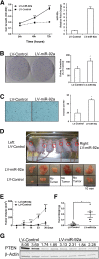
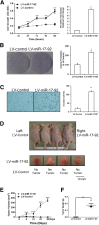
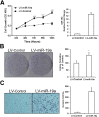
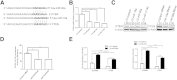
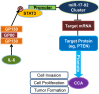
miR-17-92 is an oncogenic miRNA cluster implicated in the development of several cancers; however, it remains unknown whether the miR-17-92 cluster is able to regulate cholangiocarcinogenesis. This study was designed to investigate the biological functions and molecular mechanisms of the miR-17-92 cluster in cholangiocarcinoma. In situ hybridization and quantitative RT-PCR analysis showed that the miR-17-92 cluster is highly expressed in human cholangiocarcinoma cells compared with the nonneoplastic biliary epithelial cells. Forced overexpression of the miR-17-92 cluster or its members, miR-92a and miR-19a, in cultured human cholangiocarcinoma cells enhanced tumor cell proliferation, colony formation, and invasiveness, in vitro. Overexpression of the miR-17-92 cluster or miR-92a also enhanced cholangiocarcinoma growth in vivo in hairless outbred mice with severe combined immunodeficiency (SHO-Prkdc(scid)Hr(hr)). The tumor-suppressor, phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN), was identified as a bona fide target of both miR-92a and miR-19a in cholangiocarcinoma cells via sequence prediction, 3' untranslated region luciferase activity assay, and Western blot analysis. Accordingly, overexpression of the PTEN open reading frame protein (devoid of 3' untranslated region) prevented miR-92a- or miR-19a-induced cholangiocarcinoma cell growth. Microarray analysis revealed additional targets of the miR-17-92 cluster in human cholangiocarcinoma cells, including APAF-1 and PRDM2. Moreover, we observed that the expression of the miR-17-92 cluster is regulated by IL-6/Stat3, a key oncogenic signaling pathway pivotal in cholangiocarcinogenesis. Taken together, our findings disclose a novel IL-6/Stat3-miR-17-92 cluster-PTEN signaling axis that is crucial for cholangiocarcinogenesis and tumor progression.
Copyright © 2014 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 inhibits PTEN and promotes experimental cholangiocarcinogenesis and tumor progression.Gastroenterology. 2011 Jun;140(7):2084-94. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.02.056. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21354147 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN and PDCD4 are bona fide targets of microRNA-21 in human cholangiocarcinoma.Chin Med Sci J. 2012 Jun;27(2):65-72. Chin Med Sci J. 2012. PMID: 22770403
-
miR-21 targets 15-PGDH and promotes cholangiocarcinoma growth.Mol Cancer Res. 2014 Jun;12(6):890-900. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0419. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Mol Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24699315 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-92a promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer metastasis.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jul;51(1):235-244. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.3999. Epub 2017 May 16. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28534966
-
Insights into the role of STAT3 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2022 May;25(5):171. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12687. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 35302174 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miRNAs regulated by estrogens, tamoxifen, and endocrine disruptors and their downstream gene targets.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Dec 15;418 Pt 3(0 3):273-97. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.01.035. Epub 2015 Feb 3. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25659536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of microRNAs in Wilms' tumors.Tumour Biol. 2016 Feb;37(2):1445-50. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4514-8. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26634744 Review.
-
MiR-17-92 cluster promotes hepatocarcinogenesis.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Oct;36(10):1213-22. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv112. Epub 2015 Aug 1. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26233958 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Models for Cholangiocarcinoma-What Can We Learn for Human Disease?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 15;21(14):4993. doi: 10.3390/ijms21144993. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32679791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin 6 decreases nociceptor expression of the potassium channel KV1.4 in a rat model of hand-arm vibration syndrome.Pain. 2019 Aug;160(8):1876-1882. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001570. Pain. 2019. PMID: 31335655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Filipowicz W., Bhattacharyya S.N., Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:102–114. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Lewis B.P., Shih I.H., Jones-Rhoades M.W., Bartel D.P., Burge C.B. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell. 2003;115:787–798. - PubMed
-
- Lu J., Getz G., Miska E.A., Alvarez-Saavedra E., Lamb J., Peck D., Sweet-Cordero A., Ebert B.L., Mak R.H., Ferrando A.A., Downing J.R., Jacks T., Horvitz H.R., Golub T.R. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

