An exploratory double-blind, randomized clinical trial with selisistat, a SirT1 inhibitor, in patients with Huntington's disease
- PMID: 25223731
- PMCID: PMC4345957
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.12512
An exploratory double-blind, randomized clinical trial with selisistat, a SirT1 inhibitor, in patients with Huntington's disease
Abstract
Aims: Selisistat, a selective SirT1 inhibitor is being developed as a potentially disease-modifying therapeutic for Huntington's disease (HD). This was the first study of selisistat in HD patients and was primarily aimed at development of pharmacodynamic biomarkers.
Methods: This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre exploratory study. Fifty-five male and female patients in early stage HD were randomized to receive 10 mg or 100 mg of selisistat or placebo once daily for 14 days. Blood sampling, clinical and safety assessments were conducted throughout the study. Candidate pharmacodynamic markers included circulating soluble huntingtin and innate immune markers.
Results: Selisistat was found to be safe and well tolerated, and systemic exposure parameters showed that the average steady-state plasma concentration achieved at the 10 mg dose level (125 nm) was comparable with the IC50 for SirT1 inhibition. No adverse effects on motor, cognitive or functional readouts were recorded. While circulating levels of soluble huntingtin were not affected by selisistat in this study, the biological samples collected have allowed development of assay technology for use in future studies. No effects on innate immune markers were seen.
Conclusions: Selisistat was found to be safe and well tolerated in early stage HD patients at plasma concentrations within the anticipated therapeutic concentration range.
Keywords: Huntington's disease; SirT1 inhibition; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics; selisistat.
© 2014 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
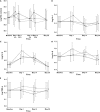
 , 10 mg selisistat;
, 10 mg selisistat;  , 100 mg selisistat;
, 100 mg selisistat;  , placebo. Model predicted values and 95% confidence intervals of estimated log plasma cytokine levels by group at each time point: (B) log IL-1, (C) log IL-6, (D) IL-8 and (E) TNF-α
, placebo. Model predicted values and 95% confidence intervals of estimated log plasma cytokine levels by group at each time point: (B) log IL-1, (C) log IL-6, (D) IL-8 and (E) TNF-αSimilar articles
-
Safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacogenomics and QT concentration-effect modelling of the SirT1 inhibitor selisistat in healthy volunteers.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Mar;79(3):477-91. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12513. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25223836 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A potent and selective Sirtuin 1 inhibitor alleviates pathology in multiple animal and cell models of Huntington's disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Jun 1;23(11):2995-3007. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu010. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 24436303 Free PMC article.
-
Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of PBT2 in Huntington's disease: a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Lancet Neurol. 2015 Jan;14(1):39-47. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70262-5. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Lancet Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25467848 Clinical Trial.
-
Tiotropium bromide. A review of its use as maintenance therapy in patients with COPD.Treat Respir Med. 2004;3(4):247-68. doi: 10.2165/00151829-200403040-00005. Treat Respir Med. 2004. PMID: 15350163 Review.
-
Investigational drugs for the management of Huntington's disease: are we there yet?Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014 Dec;23(12):1595-603. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2014.934807. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014. PMID: 25084527 Review.
Cited by
-
Virtual Screening in the Identification of Sirtuins' Activity Modulators.Molecules. 2022 Sep 1;27(17):5641. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175641. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Pathogenesis to Therapeutics: A Review of 150 Years of Huntington's Disease Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 21;24(16):13021. doi: 10.3390/ijms241613021. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of Sirtuin 2 Inhibitors Employing Photoswitchable Geometry and Aqueous Solubility.ChemMedChem. 2020 Aug 5;15(15):1480-1489. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202000148. Epub 2020 May 7. ChemMedChem. 2020. PMID: 32314517 Free PMC article.
-
SRT1720 inhibits the growth of bladder cancer in organoids and murine models through the SIRT1-HIF axis.Oncogene. 2021 Oct;40(42):6081-6092. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01999-9. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 34471236
-
Targeting Mitochondrial Sirtuins in Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases and Fibrosis.Aging Dis. 2023 Oct 1;14(5):1583-1605. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0203. Aging Dis. 2023. PMID: 37196115 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rubinsztein DC, Carmichael J. Huntington's disease: molecular basis of neurodegeneration. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2003;5:1–21. - PubMed
-
- van der Burg JM, Bjorkqvist M, Brundin P. Beyond the brain: widespread pathology in Huntington's disease. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:765–774. - PubMed
-
- Luthi-Carter R, Taylor DM, Pallos J, Lambert E, Amore A, Parker A, Moffitt H, Smith DL, Runne H, Gokce O, Kuhn A, Xiang Z, Maxwell MM, Reeves SA, Bates GP, Neri C, Thompson LM, Marsh JL, Kazantsev AG. SIRT2 inhibition achieves neuroprotection by decreasing sterol biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:7927–7932. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zuccato C, Valenza M, Cattaneo E. Molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutical targets in Huntington's disease. Physiol Rev. 2010;90:905–981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

