Sulfated glycosaminoglycans control the extracellular trafficking and the activity of the metalloprotease inhibitor TIMP-3
- PMID: 25176127
- PMCID: PMC4210636
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.07.014
Sulfated glycosaminoglycans control the extracellular trafficking and the activity of the metalloprotease inhibitor TIMP-3
Abstract
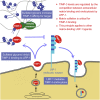
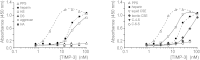
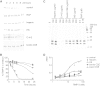
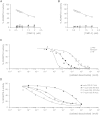
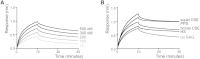
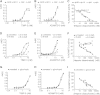
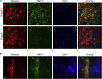
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 (TIMP-3) is an important regulator of extracellular matrix (ECM) turnover. TIMP-3 binds to sulfated ECM glycosaminoglycans or is endocytosed by cells via low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP-1). Here, we report that heparan sulfate (HS) and chondroitin sulfate E (CSE) selectively regulate postsecretory trafficking of TIMP-3 by inhibiting its binding to LRP-1. HS and CSE also increased TIMP-3 affinity for glycan-binding metalloproteinases, such as adamalysin-like metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 5 (ADAMTS-5), by reducing the dissociation rate constants. The sulfation pattern was crucial for these activities because monosulfated or truncated heparin had a reduced ability to bind to TIMP-3 and increase its affinity for ADAMTS-5. Therefore, sulfation of ECM glycans regulates the levels and inhibitory activity of TIMP-3 and modulates ECM turnover, and small mimicries of sulfated glycans may protect the tissue from the excess destruction seen in diseases such as osteoarthritis, cancer, and atherosclerosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dissecting the interaction between tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP-3) and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP-1): Development of a "TRAP" to increase levels of TIMP-3 in the tissue.Matrix Biol. 2017 May;59:69-79. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.07.004. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Matrix Biol. 2017. PMID: 27476612
-
TIMP-3 binds to sulfated glycosaminoglycans of the extracellular matrix.J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 6;275(40):31226-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M000907200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10900194
-
TIMP-3 facilitates binding of target metalloproteinases to the endocytic receptor LRP-1 and promotes scavenging of MMP-1.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 21;10(1):12067. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69008-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32694578 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin-derived heparan sulfate mimics to modulate heparan sulfate-protein interaction in inflammation and cancer.Matrix Biol. 2010 Jul;29(6):442-52. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Matrix Biol. 2010. PMID: 20416374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulfated glycosaminoglycans: their distinct roles in stem cell biology.Glycoconj J. 2017 Dec;34(6):725-735. doi: 10.1007/s10719-016-9732-9. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Glycoconj J. 2017. PMID: 27709407 Review.
Cited by
-
The dual role of the glycosaminoglycan chondroitin-6-sulfate in the development, progression and metastasis of cancer.FEBS J. 2019 May;286(10):1815-1837. doi: 10.1111/febs.14748. Epub 2019 Feb 5. FEBS J. 2019. PMID: 30637950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serpins in cartilage and osteoarthritis: what do we know?Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Apr 30;49(2):1013-1026. doi: 10.1042/BST20201231. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 33843993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Dysregulation of Metalloproteinase Activity in Osteoarthritis.Calcif Tissue Int. 2021 Sep;109(3):277-290. doi: 10.1007/s00223-020-00739-7. Epub 2020 Aug 9. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021. PMID: 32772139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of differentially expressed miRNAs and mRNAs in synovial of osteoarthritis via RNA-sequencing.BMC Med Genet. 2020 Mar 2;21(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12881-020-0978-5. BMC Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 32122327 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosaminoglycans influence enzyme activity of MMP2 and MMP2/TIMP3 complex formation - Insights at cellular and molecular level.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 20;9(1):4905. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41355-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30894640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anower-E-Khuda M.F., Matsumoto K., Habuchi H., Morita H., Yokochi T., Shimizu K., Kimata K. Glycosaminoglycans in the blood of hereditary multiple exostoses patients: Half reduction of heparan sulfate to chondroitin sulfate ratio and the possible diagnostic application. Glycobiology. 2013;23:865–876. - PubMed
-
- Asada M., Shinomiya M., Suzuki M., Honda E., Sugimoto R., Ikekita M., Imamura T. Glycosaminoglycan affinity of the complete fibroblast growth factor family. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009;1790:40–48. - PubMed
-
- Bieth J.G. Theoretical and practical aspects of proteinase inhibition kinetics. Methods Enzymol. 1995;248:59–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

