The role of the IKK complex in viral infections
- PMID: 25082354
- PMCID: PMC7108545
- DOI: 10.1111/2049-632X.12210
The role of the IKK complex in viral infections
Abstract
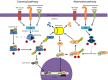
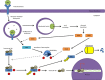
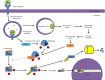
The NF-κB signal transduction pathway is a critical regulator of multiple cellular functions that ultimately shift the balance between cell survival and death. The cascade is activated by many intrinsic and extrinsic stimuli, which is transduced via adaptor proteins to phosphorylate the IκB kinase (IKK) complex, which in turn phosphorylates the inhibitory IκBα protein to undergo proteasomal degradation and sets in motion nuclear events in response to the initial stimulus. Viruses are important modulators of the NF-κB cascade and have evolved multiple mechanisms to activate or inhibit this pathway in a manner conducive to viral multiplication and establishment of a productive infectious cycle. This is a subject of extensive research by multiple laboratories whereby unraveling the interactions between specific viral components and members of the NF-κB signal transduction cascade can shed unique perspectives on infection associated pathogenesis and novel therapeutic targets. In this review, we highlight the interactions between components of the IKK complex and multiple RNA and DNA viruses with the emphasis on mechanisms by which the interaction feeds the infection. Understanding these interactions will shed light on the exploitative capabilities of viruses to maintain an environment favorable for a productive infection.
Keywords: IKK complex; host response; viral proteins.
© 2014 Federation of European Microbiological Societies. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Innate immune evasion strategies of DNA and RNA viruses.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016 Aug;32:113-119. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2016.05.015. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27288760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of antiviral innate immune signaling and viral evasion following viral genome sensing.Exp Mol Med. 2021 Nov;53(11):1647-1668. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00691-y. Epub 2021 Nov 16. Exp Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34782737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Kinase-Mediated Decision Between the Life and Death.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1275:1-33. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-49844-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33539010
-
Molluscum Contagiosum Virus MC159 Abrogates cIAP1-NEMO Interactions and Inhibits NEMO Polyubiquitination.J Virol. 2017 Jul 12;91(15):e00276-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00276-17. Print 2017 Aug 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28515292 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of Inflammasomes in Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Nasopharyngeal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 8;13(8):1786. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081786. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33918087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molluscum Contagiosum Virus Protein MC008 Targets NF-κB Activation by Inhibiting Ubiquitination of NEMO.J Virol. 2023 Mar 30;97(3):e0010823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00108-23. Epub 2023 Mar 14. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 36916940 Free PMC article.
-
Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus nsP3 Phosphorylation Can Be Mediated by IKKβ Kinase Activity and Abrogation of Phosphorylation Inhibits Negative-Strand Synthesis.Viruses. 2020 Sep 13;12(9):1021. doi: 10.3390/v12091021. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32933112 Free PMC article.
-
Transient blockade of TBK1/IKKε allows efficient transduction of primary human natural killer cells with vesicular stomatitis virus G-pseudotyped lentiviral vectors.Cytotherapy. 2021 Sep;23(9):787-792. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2021.04.010. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Cytotherapy. 2021. PMID: 34119434 Free PMC article.
-
S100A4 suppresses cancer stem cell proliferation via interaction with the IKK/NF-κB signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2018 Jul 25;18(1):763. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4563-7. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30045697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amici C, Rossi A, Costanzo A, Ciafre S, Marinari B, Balsamo M, Levrero M & Santoro MG (2006) Herpes simplex virus disrupts NF‐kappaB regulation by blocking its recruitment on the IkappaBalpha promoter and directing the factor on viral genes. J Biol Chem 281: 7110–7117. - PubMed
-
- DeLuca C, Petropoulos L, Zmeureanu D & Hiscott J (1999) Nuclear IkappaBbeta maintains persistent NF‐kappaB activation in HIV‐1‐infected myeloid cells. J Biol Chem 274: 13010–13016. - PubMed
-
- Diamant G & Dikstein R (2013) Transcriptional control by NF‐κB: elongation in focus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1829: 937–945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

