Association of sports drinks with weight gain among adolescents and young adults
- PMID: 25044989
- PMCID: PMC4180814
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.20845
Association of sports drinks with weight gain among adolescents and young adults
Abstract
Objective: Sales of regular soda were declining, but sales of other sweetened beverages, such as sports drinks, were increasing. Our objective was to determine the prospective associations between sports drinks and body mass index (BMI) gains among adolescents and young adults.
Methods: 4121 females and 3438 males in the Growing Up Today Study II, aged 9-16 in 2004, from across the United States were followed prospectively. Data were collected by questionnaire in 2004, 2006, 2008, and 2011. Servings per day of various beverages were assessed with a food frequency questionnaire.
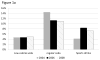
Results: Among the girls, each serving per day of sports drink predicted an increase of 0.3 BMI units (95% confidence interval (CI) CI 0.03-0.54) more than their peers over the next 2-3 years. Among the males, each serving of sports drinks predicted a 0.33 BMI (95% CI 0.09, 0.66) increase. In addition, boys who increased their intake over the 2-3 year interval gained significantly more than their peers during the same time interval.
Conclusions: Intake of sports drinks predicted larger increases in BMI among both females and males. Our results suggest that school policies focused on obesity prevention should be augmented to restrict sports drinks.
Copyright © 2014 The Obesity Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare
Figures

Comment in
-
Are the results likely biased toward the null?Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014 Nov;22(11):2326. doi: 10.1002/oby.20857. Epub 2014 Jul 31. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014. PMID: 25077972 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response to "are the results likely biased toward the null?".Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014 Nov;22(11):2327. doi: 10.1002/oby.20864. Epub 2014 Aug 18. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014. PMID: 25137625 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Association between adolescents' consumption of total and different types of sugar-sweetened beverages with oral health impacts and weight status.Aust N Z J Public Health. 2018 Feb;42(1):22-26. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12749. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Aust N Z J Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29165908
-
Beverage intake among preschool children and its effect on weight status.Pediatrics. 2006 Oct;118(4):e1010-8. doi: 10.1542/peds.2005-2348. Pediatrics. 2006. PMID: 17015497
-
[Consumption of sweetened, energy and alcoholic beverages among college students in the México-US border].Nutr Hosp. 2014 Sep 28;31(1):191-5. doi: 10.3305/nh.2015.31.1.8094. Nutr Hosp. 2014. PMID: 25561110 Spanish.
-
Indian Academy of Pediatrics Guidelines on the Fast and Junk Foods, Sugar Sweetened Beverages, Fruit Juices, and Energy Drinks.Indian Pediatr. 2019 Oct 15;56(10):849-863. Epub 2019 Aug 10. Indian Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31441436 Review.
-
Sports drinks and energy drinks for children and adolescents: are they appropriate?Pediatrics. 2011 Jun;127(6):1182-9. doi: 10.1542/peds.2011-0965. Epub 2011 May 29. Pediatrics. 2011. PMID: 21624882 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined Dyslipidemia in Children and Adolescents: a Proposed New Management Approach.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2023 May;25(5):237-245. doi: 10.1007/s11883-023-01099-x. Epub 2023 Apr 14. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2023. PMID: 37058165 Review.
-
Tolerable upper intake level for dietary sugars.EFSA J. 2022 Feb 28;20(2):e07074. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2022.7074. eCollection 2022 Feb. EFSA J. 2022. PMID: 35251356 Free PMC article.
-
Low-energy sweeteners and body weight: a citation network analysis.BMJ Nutr Prev Health. 2021 Apr 1;4(1):319-332. doi: 10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000210. eCollection 2021. BMJ Nutr Prev Health. 2021. PMID: 34308140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sexual orientation and gender identity disparities in co-occurring depressive symptoms and probable substance use disorders in a national cohort of young adults.Addict Behav. 2021 Jun;117:106817. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2021.106817. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Addict Behav. 2021. PMID: 33626483 Free PMC article.
-
Perspective: Chaos in a Bottle-A Critical Evaluation of Beverage Categorization in Nutrition Research.Adv Nutr. 2020 Nov 16;11(6):1414-1428. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmaa068. Adv Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32556223 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mintel. Sports Drinks - US. Mintel Market Research Reports Database; 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

