Insulin action in brain regulates systemic metabolism and brain function
- PMID: 24931034
- PMCID: PMC4066341
- DOI: 10.2337/db14-0568
Insulin action in brain regulates systemic metabolism and brain function
Abstract
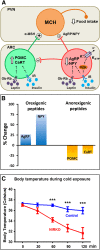
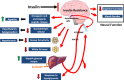
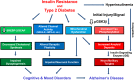
Insulin receptors, as well as IGF-1 receptors and their postreceptor signaling partners, are distributed throughout the brain. Insulin acts on these receptors to modulate peripheral metabolism, including regulation of appetite, reproductive function, body temperature, white fat mass, hepatic glucose output, and response to hypoglycemia. Insulin signaling also modulates neurotransmitter channel activity, brain cholesterol synthesis, and mitochondrial function. Disruption of insulin action in the brain leads to impairment of neuronal function and synaptogenesis. In addition, insulin signaling modulates phosphorylation of tau protein, an early component in the development of Alzheimer disease. Thus, alterations in insulin action in the brain can contribute to metabolic syndrome, and the development of mood disorders and neurodegenerative diseases.
© 2014 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of insulin receptor signaling in the brain.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Mar;16(2):59-65. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2005.01.008. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2005. PMID: 15734146 Review.
-
Brain Insulin Signaling Is Increased in Insulin-Resistant States and Decreases in FOXOs and PGC-1α and Increases in Aβ1-40/42 and Phospho-Tau May Abet Alzheimer Development.Diabetes. 2016 Jul;65(7):1892-903. doi: 10.2337/db15-1428. Epub 2016 Feb 19. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 26895791 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism: A Novel Shared Link between Diabetes Mellitus and Alzheimer's Disease.J Diabetes Res. 2020 Jan 29;2020:4981814. doi: 10.1155/2020/4981814. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 32083135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin action in the brain regulates both central and peripheral functions.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Jul 1;321(1):E156-E163. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00642.2020. Epub 2021 May 31. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34056920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin and the brain.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2013 Mar 1;9(2):102-16. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2013. PMID: 23231032 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin resistance predicts medial temporal hypermetabolism in mild cognitive impairment conversion to Alzheimer disease.Diabetes. 2015 Jun;64(6):1933-40. doi: 10.2337/db14-1507. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 25576061 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the Modular Similarities and Differences Among Alzheimer's Disease, Vascular Dementia, and Parkinson's Disease in Genomic Networks.Neuromolecular Med. 2022 Jun;24(2):125-138. doi: 10.1007/s12017-021-08670-2. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Neuromolecular Med. 2022. PMID: 34117614
-
Central Acting Hsp10 Regulates Mitochondrial Function, Fatty Acid Metabolism, and Insulin Sensitivity in the Hypothalamus.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Apr 30;10(5):711. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050711. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33946318 Free PMC article.
-
Increased GABA concentrations in type 2 diabetes mellitus are related to lower cognitive functioning.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Sep;95(36):e4803. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004803. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27603392 Free PMC article.
-
Hierarchical glucocorticoid-endocannabinoid interplay regulates the activation of the nucleus accumbens by insulin.Brain Res Bull. 2016 Jun;124:222-30. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.05.009. Epub 2016 May 18. Brain Res Bull. 2016. PMID: 27208730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belfiore A, Frasca F, Pandini G, Sciacca L, Vigneri R. Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease. Endocr Rev 2009;30:586–623 - PubMed
-
- Fernandez AM, Torres-Alemán I. The many faces of insulin-like peptide signalling in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2012;13:225–239 - PubMed
-
- Zhao WQ, Chen H, Quon MJ, Alkon DL. Insulin and the insulin receptor in experimental models of learning and memory. Eur J Pharmacol 2004;490:71–81 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

