Constitutive activation of IKK2/NF-κB impairs osteogenesis and skeletal development
- PMID: 24618907
- PMCID: PMC3949987
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091421
Constitutive activation of IKK2/NF-κB impairs osteogenesis and skeletal development
Abstract
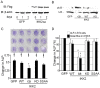
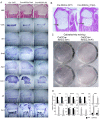
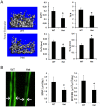
Pathologic conditions impair bone homeostasis. The transcription factor NF-κB regulates bone homeostasis and is central to bone pathologies. Whereas contribution of NF-κB to heightened osteoclast activity is well-documented, the mechanisms underlying NF-κB impact on chondrocytes and osteoblasts are scarce. In this study, we examined the effect of constitutively active IKK2 (IKK2ca) on chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation. We show that retroviral IKK2ca but not GFP, IKK2WT, or the inactive IKK2 forms IKK2KM and IKK2SSAA, strongly suppressed osteogenesis and chondrogenesis, in vitro. In order to explore the effect of constitutive NF-κB activation on bone formation in vivo, we activated this pathway in a conditional fashion. Specifically, we crossed the R26StopIKK2ca mice with mice carrying the Col2-cre in order to express IKK2ca in osteoblasts and chondrocytes. Both chondrocytes and osteoblasts derived from Col2Cre/IKK2ca expressed IKK2ca. Mice were born alive yet died shortly thereafter. Histologically, newborn Col2Cre+/RosaIKK2ca heterozygotes (Cre+IKK2ca_w/f (het)) and homozygotes (Cre+IKK2ca_f/f (KI)) showed smaller skeleton, deformed vertebrate and reduced or missing digit ossification. The width of neural arches, as well as ossification in vertebral bodies of Cre+IKK2ca_w/f and Cre+IKK2ca_f/f, was reduced or diminished. H&E staining of proximal tibia from new born pups revealed that Cre+IKK2ca_f/f displayed disorganized hypertrophic zones within the smaller epiphysis. Micro-CT analysis indicated that 4-wk old Cre+IKK2ca_w/f has abnormal trabecular bone in proximal tibia compared to WT littermates. Mechanistically, ex-vivo experiments showed that expression of differentiation markers in calvarial osteoblasts derived from newborn IKK2ca knock-in mice was diminished compared to WT-derived cells. In situ hybridization studies demonstrated that the hypertrophic chondrocyte marker type-X collagen, the pre-hypertrophic chondrocyte markers Indian hedgehog and alkaline phosphatase, and the early markers Aggrecan and type-II collagen were reduced in Cre+IKK2ca_w/f and Cre+IKK2ca_f/f mice. Altogether, the in-vitro, in vivo and ex-vivo evidence suggest that IKK2ca perturbs osteoblast and chondrocyte maturation and impairs skeletal development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Core binding factor beta (Cbfβ) controls the balance of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation by upregulating Indian hedgehog (Ihh) expression and inhibiting parathyroid hormone-related protein receptor (PPR) expression in postnatal cartilage and bone formation.J Bone Miner Res. 2014 Jul;29(7):1564-1574. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2275. J Bone Miner Res. 2014. PMID: 24821091 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate activation of IKK2-NF-kB in unstressed adult mouse liver induces cytoprotective genes and lipogenesis without apparent signs of inflammation or fibrosis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2015 Jul 30;15:94. doi: 10.1186/s12876-015-0325-z. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26219821 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive activation of the alternative NF-κB pathway disturbs endochondral ossification.Bone. 2019 Apr;121:29-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2019.01.002. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Bone. 2019. PMID: 30611922
-
Functions of nuclear factor kappaB in bone.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Mar;1192:367-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05315.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20392262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actions of hedgehog proteins on skeletal cells.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1999;10(4):477-86. doi: 10.1177/10454411990100040401. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1999. PMID: 10634584 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased NF-kB activity in osteoprogenitor-lineage cells impairs the balance of bone versus fat in the marrow of skeletally mature mice.Regen Eng Transl Med. 2020 Mar;6:69-77. doi: 10.1007/s40883-019-00112-7. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Regen Eng Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32377560 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting angiogenesis for fracture nonunion treatment in inflammatory disease.Bone Res. 2021 Jun 7;9(1):29. doi: 10.1038/s41413-021-00150-4. Bone Res. 2021. PMID: 34099632 Free PMC article.
-
SOST/Sclerostin Improves Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis and Inhibits MMP2/3 Expression After Injury.J Bone Miner Res. 2018 Jun;33(6):1105-1113. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3397. Epub 2018 Apr 2. J Bone Miner Res. 2018. PMID: 29377313 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic inflammation triggered by the NLRP3 inflammasome in myeloid cells promotes growth plate dysplasia by mesenchymal cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 7;7(1):4880. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05033-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28687790 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Tendon-to-Bone Healing via IKKβ Inhibition in a Rat Rotator Cuff Model.Am J Sports Med. 2021 Mar;49(3):780-789. doi: 10.1177/0363546520985203. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Am J Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 33507808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanaka Y, Nakayamada S, Okada Y (2005) Osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone remodeling and inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 4: 325–328. - PubMed
-
- Teitelbaum SL, Ross FP (2003) Genetic regulation of osteoclast development and function. Nat Rev Genet 4: 638–649. - PubMed
-
- Zaidi M (2007) Skeletal remodeling in health and disease. Nature medicine 13: 791–801. - PubMed
-
- Rodan GA, Martin TJ (2000) Therapeutic approaches to bone diseases. Science (New York, NY) 289: 1508–1514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

