Validity of SW982 synovial cell line for studying the drugs against rheumatoid arthritis in fluvastatin-induced apoptosis signaling model
- PMID: 24604047
- PMCID: PMC3994728
Validity of SW982 synovial cell line for studying the drugs against rheumatoid arthritis in fluvastatin-induced apoptosis signaling model
Abstract
Background & objectives: To study effects of drugs against rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synoviocytes or fibroblast like synoviocytes (FLS) are used. To overcome the drawbacks of using FLS, this study was conducted to show the validity of SW982 synovial cell line in RA study.
Methods: 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, Annexin V propidium iodide (PI) staining, mitochondrial membrane potential assay, Triton X-114 Phase partitioning, and immunolot for apoptosis signaling in SW982 human synovial cell line were performed.
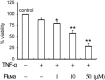
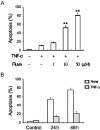
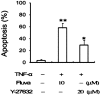
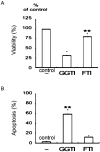
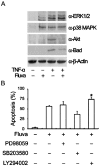
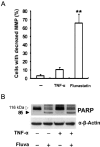
Results: Fluvastatin induced apoptosis in a dose- and time-dependent manner in TNFα -stimulated SW982 human synovial cells. A geranylgeranylpyrophosphate (GGPP) inhibitor, but not a farnesylpyrophosphate (FPP) inhibitor, induced apoptosis, and fluvastatin-induced apoptosis was associated with the translocation of isoprenylated RhoA and Rac1 proteins from the cell membrane to the cytosol. Fluvastatin-induced downstream apoptotic signals were associated with inhibition of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway. Accordingly, 89 kDa apoptotic cleavage fragment of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) was detected.
Interpretation & conclusions: Collectively, our data indicate that fluvastatin induces apoptotic cell death in TNFα-stimulated SW982 human synovial cells through the inactivation of the geranylgerenylated membrane fraction of RhoA and Rac1 proteins and the subsequent inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. This finding shows the validity of SW982 cell line for RA study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apoptosis of rheumatoid synovial cells by statins through the blocking of protein geranylgeranylation: a potential therapeutic approach to rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Feb;54(2):579-86. doi: 10.1002/art.21564. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16447234
-
Mitomycin C induces apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via a mitochondrial-mediated pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(3):1125-36. doi: 10.1159/000373938. Epub 2015 Feb 6. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25766525
-
The effects of arctigenin on human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Pharm Biol. 2015 Aug;53(8):1118-23. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2014.960945. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Pharm Biol. 2015. PMID: 25609147
-
Apoptosis Induction of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes Is an Important Molecular-Mechanism for Herbal Medicine along with its Active Components in Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis.Biomolecules. 2019 Nov 28;9(12):795. doi: 10.3390/biom9120795. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31795133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin K and rheumatoid arthritis.IUBMB Life. 2008 Jun;60(6):355-61. doi: 10.1002/iub.41. IUBMB Life. 2008. PMID: 18484089 Review.
Cited by
-
Epithelium-specific Ets transcription factor-1 acts as a negative regulator of cyclooxygenase-2 in human rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.Cell Biosci. 2016 Jun 16;6:43. doi: 10.1186/s13578-016-0105-7. eCollection 2016. Cell Biosci. 2016. PMID: 27313839 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Pathogenetic Role of Antimicrobial Peptides Carried by Extracellular Vesicles in an in vitro Psoriatic Model.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Sep 16;15:5387-5399. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S373150. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36147689 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalein Induces Apoptosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts through Inactivation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Sep 7;2022:3643265. doi: 10.1155/2022/3643265. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36118088 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Arthritic and Anti-Cancer Activities of Polyphenols: A Review of the Most Recent In Vitro Assays.Life (Basel). 2023 Jan 28;13(2):361. doi: 10.3390/life13020361. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rho GTPase signaling in rheumatic diseases.iScience. 2021 Dec 14;25(1):103620. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103620. eCollection 2022 Jan 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 35005558 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Komatsu N, Takayanagi H. Bone and cartilage destruction in RA and its intervention. Bone and cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Calcium. 2012;22:179–85. - PubMed
-
- Niedermeier M, Pap T, Korb A. Therapeutic opportunities in fibroblasts in inflammatory arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010;24:527–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
