Extracellular caspase-6 drives murine inflammatory pain via microglial TNF-α secretion
- PMID: 24531553
- PMCID: PMC3934175
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI72230
Extracellular caspase-6 drives murine inflammatory pain via microglial TNF-α secretion
Abstract
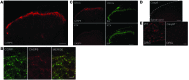
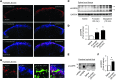
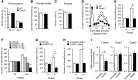
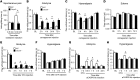
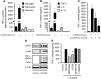
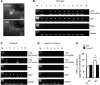
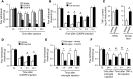
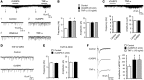
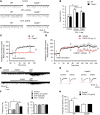
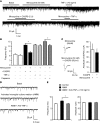
Increasing evidence indicates that the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain is mediated through spinal cord microglia activation. The intracellular protease caspase-6 (CASP6) is known to regulate neuronal apoptosis and axonal degeneration; however, the contribution of microglia and CASP6 in modulating synaptic transmission and pain is unclear. Here, we found that CASP6 is expressed specifically in C-fiber axonal terminals in the superficial spinal cord dorsal horn. Animals exposed to intraplantar formalin or bradykinin injection exhibited CASP6 activation in the dorsal horn. Casp6-null mice had normal baseline pain, but impaired inflammatory pain responses. Furthermore, formalin-induced second-phase pain was suppressed by spinal injection of CASP6 inhibitor or CASP6-neutralizing antibody, as well as perisciatic nerve injection of CASP6 siRNA. Recombinant CASP6 (rCASP6) induced marked TNF-α release in microglial cultures, and most microglia within the spinal cord expressed Tnfa. Spinal injection of rCASP6 elicited TNF-α production and microglia-dependent pain hypersensitivity. Evaluation of excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) revealed that rCASP6 rapidly increased synaptic transmission in spinal cord slices via TNF-α release. Interestingly, the microglial inhibitor minocycline suppressed rCASP6 but not TNF-α-induced synaptic potentiation. Finally, rCASP6-activated microglial culture medium increased EPSCs in spinal cord slices via TNF-α. Together, these data suggest that CASP6 released from axonal terminals regulates microglial TNF-α secretion, synaptic plasticity, and inflammatory pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TNF-α Differentially Regulates Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampus and Spinal Cord by Microglia-Dependent Mechanisms after Peripheral Nerve Injury.J Neurosci. 2017 Jan 25;37(4):871-881. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2235-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28123022 Free PMC article.
-
JNK-induced MCP-1 production in spinal cord astrocytes contributes to central sensitization and neuropathic pain.J Neurosci. 2009 Apr 1;29(13):4096-108. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3623-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19339605 Free PMC article.
-
Minocycline, a microglial inhibitor, blocks spinal CCL2-induced heat hyperalgesia and augmentation of glutamatergic transmission in substantia gelatinosa neurons.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Jan 10;11:7. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 24405660 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial Signaling in Chronic Pain with a Special Focus on Caspase 6, p38 MAP Kinase, and Sex Dependence.J Dent Res. 2016 Sep;95(10):1124-31. doi: 10.1177/0022034516653604. Epub 2016 Jun 15. J Dent Res. 2016. PMID: 27307048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unconventional Role of Caspase-6 in Spinal Microglia Activation and Chronic Pain.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:9383184. doi: 10.1155/2017/9383184. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 28270702 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preemptive Intravenous Nalbuphine for the Treatment of Post-Operative Visceral Pain: A Multicenter, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Clinical Trial.Pain Ther. 2021 Dec;10(2):1155-1169. doi: 10.1007/s40122-021-00275-8. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Pain Ther. 2021. PMID: 34089152 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on mechanism of Chinese Kaiqiao herbs in management of neuropathic pain.Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Nov 25;51(5):523-533. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2022-0351. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36581573 Free PMC article. Review. English.
-
Protein Kinase C Lambda Mediates Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a-Dependent Cortical Synaptic Plasticity and Pain Hypersensitivity.J Neurosci. 2019 Jul 17;39(29):5773-5793. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0213-19.2019. Epub 2019 May 17. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31101759 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Microglial Signaling Pathways: New Insights in the Modulation of Neuropathic Pain.Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(26):2908-2928. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666160607120124. Curr Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27281131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nociceptor Sensory Neuron-Immune Interactions in Pain and Inflammation.Trends Immunol. 2017 Jan;38(1):5-19. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Oct 25. Trends Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27793571 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

